论文标题:Peptide ion channel toxins from the bootlace worm, the longest animal on Earth
期刊:Scientific Reports
作者:Erik Jacobsson, Hakan S. Andersson, Malin Strand, Steve Peigneur, Camilla Eriksson, Henrik Loden, Mohammadreza Shariatgorji, Per E. Andren, Eline K. M. Lebbe, K. Johan Rosengren, Jan Tytgat, Ulf Goransson
发表时间:2018/03/22
数字识别码: 10.1038/s41598-018-22305-w
原文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-22305-w?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-MixedBrand-multijournal-Multidisciplinary-China&utm_campaign=ORG_USG_JRCN_RL_article_promotion_sciencenet_Oct_5th
动物毒液中的多肽在制药,药理学工具,生物技术和农业等领域具有广泛的应用。近期在发表于《科学报告》的一篇文章Peptide ion channel toxins from the bootlace worm, the longest animal on Earth中,来自瑞典乌普萨拉大学的Ulf Göransson及其研究团队报道了一系列新的来自纽形蠕虫的胱氨酸结肽,这一系列的多肽对电压门控钠离子通道有很强的活性反应。
这些被称为α-纽虫肽(α-nemertides)的毒素发现于巨纵沟纽虫(Lineuslongissimus)的表皮粘液中,巨纵沟纽虫也被称为“鞋带”虫,是地球上最长的动物。研究者们从这种毒素中分离出了含量最高的多肽,即具有31个氨基酸残基的 α-1,对它进行了合成并通过核磁共振确定了其三维结构。研究者对17种纽虫进行转录组分析后发现了八种α-纽虫肽,主要存在于Lineus属。α-1在1 µg/kg (~300 pmol/kg)的剂量下可导致普通滨蟹(Carcinusmaenas)瘫痪死亡。在低纳摩尔浓度下可对无脊椎动物的电压门控钠离子通道(如德国小蠊的Nav1)产生显著效应。
相对于人类的钠离子通道,α-1对昆虫的钠离子通道有极强的选择性,这表明,α-纽虫肽有潜力用来制备生物杀虫剂。
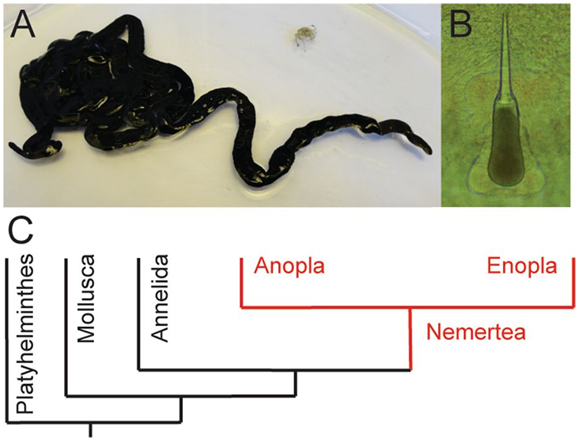
图1:巨纵沟纽虫(Lineuslongissimus )及其种系发生
摘要:Polypeptides from animal venoms have found important uses as drugs, pharmacological tools, and within biotechnological and agricultural applications. We here report a novel family of cystine knot peptides from nemertean worms, with potent activity on voltage-gated sodium channels. These toxins, named the α-nemertides, were discovered in the epidermal mucus of Lineuslongissimus, the ‘bootlace worm’ known as the longest animal on earth. The most abundant peptide, the 31-residue long α-1, was isolated, synthesized, and its 3D NMR structure determined. Transcriptome analysis including 17 species revealed eight α-nemertides, mainly distributed in the genus Lineus. α-1 caused paralysis and death in green crabs (Carcinusmaenas) at 1 µg/kg (~300 pmol/kg). It showed profound effect on invertebrate voltage-gated sodium channels (e.g. Blattellagermanica Nav1) at low nanomolar concentrations. Strong selectivity for insect over human sodium channels indicates that α-nemertides can be promising candidates for development of bioinsecticidal agents.
阅读论文全文请访问:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-22305-w?utm_source=Other_website&utm_medium=Website_links&utm_content=RenLi-MixedBrand-multijournal-Multidisciplinary-China&utm_campaign=ORG_USG_JRCN_RL_article_promotion_sciencenet_Oct_5th
期刊介绍:Scientific Reports (https://www.nature.com/srep/) is an online, open access journal from the publishers of Nature. We publish scientifically valid primary research from all areas of the natural and clinical sciences.
The 2017 journal metrics for Scientific Reports are as follows:
•2-year impact factor: 4.122
•5-year impact factor: 4.609
•Immediacy index: 0.576
•Eigenfactor® score: 0.71896
•Article Influence Score: 1.356
•2-year Median: 2
(来源:科学网)