|
|
|
|
|
FMD 论文速览:表观遗传学在自身免疫相关性皮肤病中的重要作用 |
|
|
论文标题:The critical importance of epigenetics in autoimmune-related skin diseases
期刊: Frontiers of Medicine
作者:Lingyu Gao , Qianjin Lu
发表时间:15 Feb 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0980-8
微信链接:点击此处阅读微信文章
导 读
中国医学科学院北京协和医学院皮肤病研究所、中国医学科学院免疫性皮肤病基础与转化研究重点实验室、江苏省皮肤病与性病分子生物学重点实验室陆前进教授团队在Frontiers of Medicine发表综述论文《表观遗传学在自身免疫相关性皮肤病中的重要作用》(The critical importance of epigenetics in autoimmune-related skin diseases)。本文综述了目前最重要的自身免疫相关性皮肤病的表观遗传学研究成果,包括系统性红斑狼疮、大疱性皮肤病、银屑病和系统性硬化症。
Autoimmune-related skin diseases are a group of disorders with diverse etiology and pathophysiology involved in autoimmunity. Genetics and environmental factors may contribute to the development of these autoimmune disorders. Although the etiology and pathogenesis of these disorders are poorly understood, environmental variables that induce aberrant epigenetic regulations may provide some insights. Epigenetics is the study of heritable mechanisms that regulate gene expression without changing DNA sequences. The most important epigenetic mechanisms are DNA methylation, histone modification, and noncoding RNAs. In this review, we discuss the most recent findings regarding the function of epigenetic mechanisms in autoimmune-related skin disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, bullous skin diseases, psoriasis, and systemic sclerosis. These findings will expand our understanding and highlight the possible clinical applications of precision epigenetics approaches.
自身免疫相关性皮肤病是一组与自身免疫相关的病因和病理生理机制多样的疾病。遗传和环境因素都可能导致这些自身免疫性疾病的发生。虽然这些疾病的病因和发病机制尚不清楚,但诱发异常表观遗传调控的环境变量,或许能为我们提供一些线索。表观遗传学是研究在不改变DNA序列的情况下,调控基因表达的遗传机制。其中最重要的表观遗传机制包括DNA甲基化、组蛋白修饰和非编码RNA。本综述讨论了表观遗传机制在自身免疫相关性皮肤疾病(包括系统性红斑狼疮、大疱性皮肤病、银屑病和系统性硬化症)的最新研究成果。这些发现将拓展我们的认知,并强调精准表观遗传学方法在临床上的潜在应用价值。
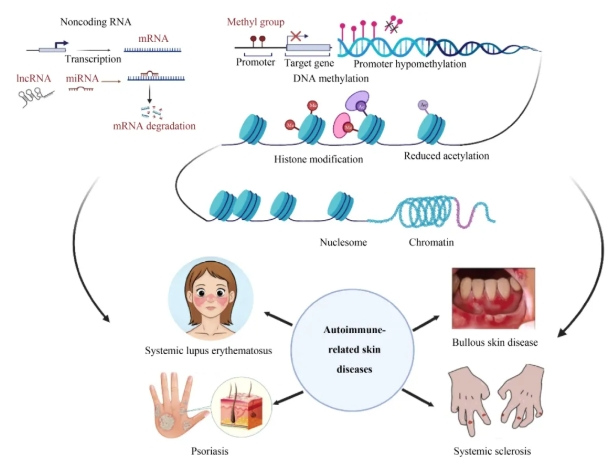
摘要图
期刊介绍
Frontiers of Medicine专注于发表临床医学和基础医学领域的最新研究成果,旨在通过全球医疗专业人员之间的交流促进健康和医疗保健的发展。该刊采用严格的同行评审和编辑流程,确保发表的文章的科学准确性、新颖性和重要性。
原文信息
标题
The critical importance of epigenetics in autoimmune-related skin diseases
作者
Lingyu Gao, Qianjin Lu
机构
Institute of Dermatology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Nanjing 210042, China; Key Laboratory of Basic and Translational Research on Immune-Mediated Skin Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Nanjing 210042, China; Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Skin Diseases and STIs, Nanjing 210042, China
通讯作者
Qianjin Lu
引用这篇文章
Lingyu Gao, Qianjin Lu. The critical importance of epigenetics in autoimmune-related skin diseases. Front. Med., 2023, 17(1): 43–57 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0980-8
https://journal.hep.com.cn/fmd/EN/10.1007/s11684-022-0980-8
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11684-022-0980-8
感谢作者对Frontiers of Medicine的信任和支持。

《前沿》系列英文学术期刊
由教育部主管、高等教育出版社主办的《前沿》(Frontiers)系列英文学术期刊,于2006年正式创刊,以网络版和印刷版向全球发行。系列期刊包括基础科学、生命科学、工程技术和人文社会科学四个主题,是我国覆盖学科最广泛的英文学术期刊群,其中12种被SCI收录,其他也被A&HCI、Ei、MEDLINE或相应学科国际权威检索系统收录,具有一定的国际学术影响力。系列期刊采用在线优先出版方式,保证文章以最快速度发表。
中国学术前沿期刊网
http://journal.hep.com.cn

特别声明:本文转载仅仅是出于传播信息的需要,并不意味着代表本网站观点或证实其内容的真实性;如其他媒体、网站或个人从本网站转载使用,须保留本网站注明的“来源”,并自负版权等法律责任;作者如果不希望被转载或者联系转载稿费等事宜,请与我们接洽。