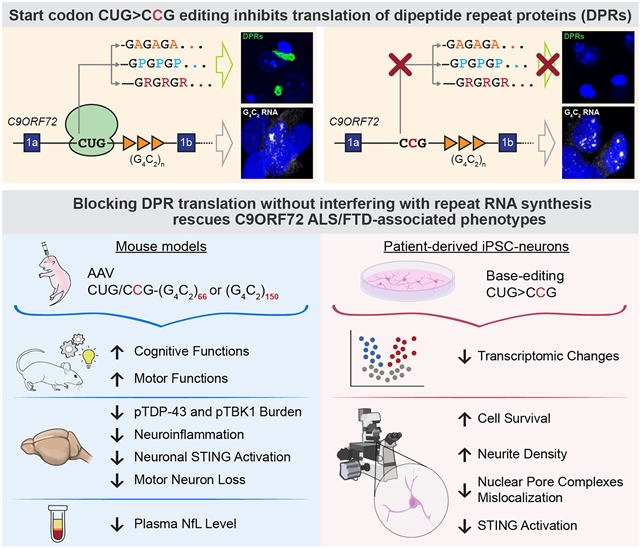
为了将RNA从DPR毒性中分离出来,该团队突变了一个CUG密码子,以启动所有三个阅读框的DPR翻译。这种突变破坏了DPR的合成,同时保留了含有重复序列的RAN的表达。尽管RNA病灶积累,但C9ORF72小鼠的行为缺陷和病理异常,包括p-TDP-43缺失、STING激活、运动神经元丢失、神经炎症和血浆神经丝浓度升高,均得到缓解。CUG密码子的碱基编辑也改善了患者诱导的多能干细胞衍生神经元的分子表型和存活,这突出了治疗靶向DPR产生而不是重复RAN的潜力。
据了解,C9ORF72中GGGGCC (G4C2)重复扩增是肌萎缩性侧索硬化症(ALS)和额颞叶痴呆(FTD)最常见的遗传突变。毒性被认为是由于重复RAN和/或二肽重复蛋白(DPRs)的积累,这些重复RAN和/或二肽重复蛋白(DPRs)是通过重复相关的非AUG(RAN)翻译从含有重复的转录物中翻译出来的。
附:英文原文
Title: Blocking RAN translation without altering repeat RNAs rescues C9ORF72-related ALS and FTD phenotypes
Author: Xin Jiang, Laure Schaeffer, Divya Patni, Tommaso Russo, Chao-Zong Lee, Corey Aguilar, Christine Marques, Karen Jansen-West, Marian Hruska-Plochan, Ananya Ray-Soni, Su Min Lim, Aaron Held, Mei Yue, Paula Castellanos Otero, Sandeep Aryal, Hortense D. A. M. Beaussant, Himanish Basu, Hiro Takakuwa, Lillian M. Daughrity, Nandini Ramesh, Paulo Da Costa, Ana Rita A. A. Quadros, Matthew Nolan, Charles Jourdan F. Reyes, Hayden Wheeler, Laura C. Moran, Grant Griesman, Benjamin Wymann, Bianca A. Trombetta, Emma Sofia Lopez-De-Silanes, Michael Canori, Gopinath Krishnan, Yasmim Vieira Souza Da Silva, Gilbert Eriani, Mark W. Albers, Steven E. Arnold, Yuyu Song, Ankur Jain, Isaac M. Chiu, Yong-Jie Zhang, Fen-Biao Gao, Brian J. Wainger, Magdalini Polymenidou, Leonard Petrucelli, Franck Martin, Clotilde Lagier-Tourenne
Issue&Volume: 2026-02-05
Abstract: GGGGCC (G4C2) repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the most common genetic cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Toxicity is thought to result from the accumulation of either repeat RNAs and/or dipeptide repeat proteins (DPRs) translated from repeat-containing transcripts through repeat-associated non-AUG (RAN) translation. To disentangle RNA from DPR toxicity, we mutated a CUG codon predominantly used to initiate DPR translation from all three reading frames. This mutation disrupted DPR synthesis while preserving the expression of repeat-containing RNAs. Despite the accumulation of RNA foci, behavioral deficits and pathological abnormalities, including p-TDP-43 inclusions, STING activation, motor neuron loss, neuroinflammation, and increased plasma neurofilament concentration, were alleviated in C9ORF72 mice. Base editing of the CUG codon also improved molecular phenotypes and survival in patient induced pluripotent stem cell–derived neurons, which highlights the potential of therapeutically targeting DPR production rather than repeat RNAs.
DOI: adv2600
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adv2600
