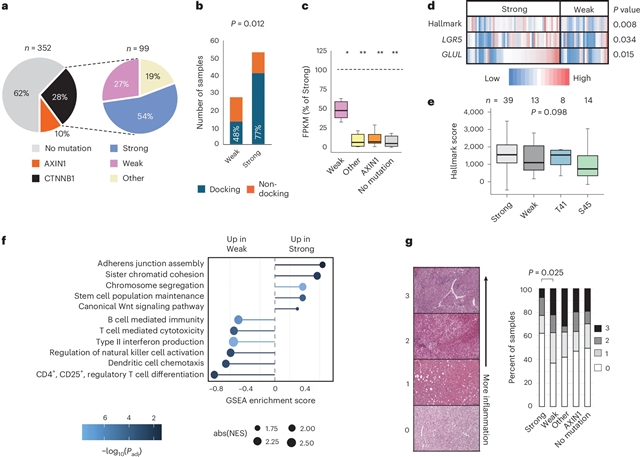
爱丁堡大学Derya D. Ozdemir课题组的一项最新研究探明了突变扫描显示致癌CTNNB1突变对信号传导有不同的影响。这一研究成果发表在2026年2月2日出版的国际学术期刊《自然—遗传学》上。
课题组人员将饱和基因组编辑与荧光报告分析相结合,量化突变热点中所有342种可能错义突变的信号表型。他们的数据定义了β-catenin degron功能的遗传要求,完善了β-TRCP识别底物的共识基序,并揭示了已知驱动突变中不同水平的信号激活。不同人体组织的肿瘤发生涉及CTNNB1突变的选择,这些突变跨越了不同的预测活性范围。在肝细胞癌中,突变效应评分区分了两种具有不同水平β-catenin信号的肿瘤亚类,较弱的突变预示着肿瘤微环境中免疫细胞的浸润程度较高。他们的工作为理解泛癌症突变热点中的突变多样性提供了一个基础,对靶向治疗具有潜在的意义。
据悉,编码β-catenin的基因CTNNB1是激活典型Wnt信号通路的致癌突变的常见靶标,通常是通过外显子3的degron热点基序内的错义突变。
附:英文原文
Title: Mutational scanning reveals oncogenic CTNNB1 mutations have diverse effects on signaling
Author: Krishna, Anagha, Meynert, Alison, Dolt, Karamjit Singh, Kelder, Martijn, Mesropian, Agavni, Ewing, Ailith, Brouwers, Conny, Claassens, Jill WC, Linssen, Margot M., Sheraz, Shahida, Taylor, Gillian CA, Gautier, Philippe, Ferrer-Vaquer, Anna, Grimes, Graeme, Becher, Hannes, Silk, Ryan, Gris-Oliver, Albert, Pinyol, Roser, Semple, Colin A., Kendall, Timothy J., Bird, Thomas Graham, Hadjantonakis, Anna-Katerina, Marsh, Joseph A., Llovet, Josep M., Hohenstein, Peter, Wood, Andrew J., Ozdemir, Derya D.
Issue&Volume: 2026-02-02
Abstract: CTNNB1, the gene encoding β-catenin, is a frequent target for oncogenic mutations activating the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, typically through missense mutations within a degron hotspot motif in exon 3. Here, we combine saturation genome editing with a fluorescent reporter assay to quantify signaling phenotypes for all 342 possible missense mutations in the mutation hotspot. Our data define the genetic requirements for β-catenin degron function, refine the consensus motif for substrate recognition by β-TRCP and reveal diverse levels of signal activation among known driver mutations. Tumorigenesis in different human tissues involves selection for CTNNB1 mutations spanning distinct ranges of predicted activity. In hepatocellular carcinoma, mutation effect scores distinguish two tumor subclasses with different levels of β-catenin signaling, and weaker mutations predict greater immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment. Our work provides a resource to understand mutational diversity within a pan-cancer mutation hotspot, with potential implications for targeted therapy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02496-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02496-5
Nature Genetics:《自然—遗传学》,创刊于1992年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:41.307
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ng/
投稿链接:https://mts-ng.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
