近日,西安交通大学郗凯团队报道了取向位诱导反铁磁耦合稳定废锂离子电池重构阴极。2026年2月11日出版的《德国应用化学》杂志发表了这项成果。
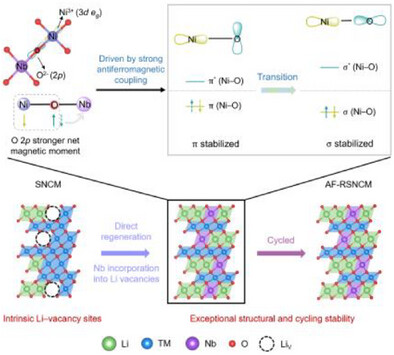
直接再生退役层状三元氧化物正极材料为资源回收与循环电池制造提供了可持续路径。然而,其长期稳定性从根本上受制于本征电子相互作用——特别是Ni 3d轨道与O 2p轨道间固有的π型杂化会引发有害的Ni迁移及岩盐相形成,最终导致容量快速衰减。
研究组利用废旧LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2(NCM)中预存的锂空位作为取向位点,在再生过程中诱导产生局部晶格应力场。由此引发的晶格扰动调制了桥接氧阴离子的自旋构型,从而触发相邻Ni阳离子与O阴离子间的反铁磁耦合。最终,Ni─O轨道杂化由弱π主导型转变为强σ主导型,Ni─O键共价特性的增强证实了这一转变。
这种强化键合框架有效抑制了循环锂化/脱锂过程中的Ni迁移及缺陷扩展。因此,再生NCM正极展现出显著提升的耐久性,在750次循环后仍保持约60%的初始容量。这些发现揭示了正极材料局域价键演化与循环可逆性间的直接关联,为稳定再生正极材料提供了新设计原则与机理认知。
附:英文原文
Title: Orientation Site-Induced Antiferromagnetic Coupling Stabilizes Reconstructed Cathode From Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries
Author: Chenzhaosha Li, Yujia He, Weiping Li, Kai Jia, Pengfei Li, Kunzhi Hou, Guorui Yang, Ming Xu, Shujiang Ding, Kai Xi
Issue&Volume: 2026-02-11
Abstract: Direct regeneration of spent layered ternary oxide cathodes offers a sustainable pathway for resource recovery and circular battery manufacturing. However, their long-term stability is fundamentally constrained by intrinsic electronic interactions. In particular, the inherent π-type hybridization between Ni 3d orbitals and O 2p orbitals facilitates detrimental Ni migration and rock-salt phase formation, ultimately leading to rapid capacity degradation. Here, we leverage the preexisting Li vacancies in spent LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 (NCM) as orientation sites to induce localized lattice stress fields during regeneration. The resulting lattice perturbation modulates the spin configuration of bridging O anions, thereby triggering antiferromagnetic coupling between adjacent Ni cations and O anions. Consequently, the Ni─O orbital hybridization transitions from weak π-dominated to robust σ-dominated interactions, as evidenced by enhanced covalent character of the Ni─O bonds. This reinforced bonding framework effectively suppresses Ni migration and defect propagation during repeated lithiation/delithiation cycles. As a result, the regenerated NCM cathode exhibits significantly improved durability, retaining ~60% of its initial capacity after 750 cycles. These findings reveal a direct correlation between the local valence bond evolution and cycling reversibility of cathode materials, offering new design principles and mechanistic insights for stabilizing regenerated cathode materials.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202522851
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202522851
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
