近日,中国科学院福建物质结构研究所林启普团队研究了基于钼硫簇超分子基质的静电限制光敏剂用于高效双光催化:氢气生成和三氟甲基化。该项研究成果发表在2025年12月30日出版的《美国化学会志》上。
提升分子光敏剂与催化单元之间的电荷转移效率,是发展先进光催化系统的关键目标与核心挑战。
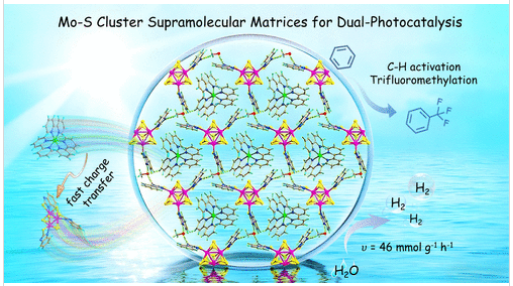
研究组提出一种晶体学自组装策略,构建了具有周期性有序结构的超分子体系Ru@MoS-MBIZ。在该结构中,阳离子光敏剂[三联吡啶钌(II)]通过静电作用固定于由阴离子钼硫簇构筑的孔腔内,实现了光捕获单元与催化单元在空间上的精准偶联。这种原子级精确排列不仅增强了结构稳定性与光吸收能力,还优化了电子结构与能级匹配,从而促进高效的电荷分离与定向电荷转移。该集成体系展现出优异的光催化产氢性能,产氢速率高达46 mmol g-1 h-1,分别是原始MoS-MBIZ与物理混合体系[Ru(bpy)3]Cl2/MoS-MBIZ的118倍和4.5倍,且性能优于多数贵金属辅助的晶态光催化剂。
尤为突出的是,该集成策略实现了从单一功能到双功能光催化的跨越,同步完成了可见光驱动的三氟甲苯三氟甲基化反应(产率>85%),底物范围覆盖25种芳(杂)环及药物分子,标志着钼硫簇在有机光合成领域的首次拓展。通过实验与理论相结合的机理研究,证实了体系内增强的电荷分离以及从钌中心到钼中心的定向电子转移过程。该研究为通过静电限域与晶体学集成构建可编程多功能光催化剂提供了范式蓝图。
附:英文原文
Title: Electrostatic Confinement of Photosensitizers within Molybdenum–Sulfur Cluster-Based Supramolecular Matrices for Efficient Dual-Photocatalysis: Hydrogen Evolution and Trifluoromethylation
Author: Hui-Li Zheng, Jian-Qiang Zhao, Xiong-Feng Ma, Jia-Wei Li, Yu-Jia Cheng, Er-Xia Chen, Jian Zhang, Qipu Lin
Issue&Volume: December 30, 2025
Abstract: Enhancing charge transfer efficiency between molecular photosensitizers and catalytic units remains a pivotal yet challenging objective in developing advanced photocatalytic systems. Herein, we present a crystallographic self-assembly strategy to construct Ru@MoS-MBIZ─a periodically ordered supramolecular architecture, wherein cationic photosensitizers, [Ru(bpy)3]2+, are electrostatically immobilized within cavities formed by anionic molybdenum–sulfur (Mo–S) clusters ([Mo3S7(MBIZ)3]–), enabling spatially defined coupling between light-harvesting and catalytic moieties. The atomically precise arrangement not only enhances structural stability and light absorption but also optimizes the electronic structure and energy-level alignment, facilitating efficient charge separation and directional charge transfer. The integrated system exhibits outstanding photocatalytic performance for hydrogen production with an impressive generation rate of 46 mmol g–1 h–1─118 and 4.5 times higher than those of pristine MoS-MBIZ and a physical mixture of [Ru(bpy)3]Cl2/MoS-MBIZ, respectively, surpassing most noble-metal-assisted crystalline photocatalysts. Notably, this integrated strategy enables a leap from single- to dual-function photocatalysis, concurrently achieving visible-light-driven trifluoromethylation with >85% yield for trifluorotoluene and a broad substrate scope covering 25 diverse (hetero)arenes and pharmaceuticals, marking the first extension of Mo–S clusters to organic photosynthesis. Mechanistic investigations through experimental and theoretical analyses confirm enhanced charge separation and directional electron transfer from Ru to Mo centers. This work establishes a blueprint for programmable multifunctional photocatalysts via electrostatic confinement and crystallographic integration.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15376
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jacs.5c15376
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
