近日,土耳其科奇大学Metin Sitti团队研究了光流体三维微加工与纳米加工。该研究于2026年1月28日发表在《自然》杂志上。
三维微纳加工技术通过精确构筑复杂三维微纳结构,为诸多领域带来革命性突破。然而,现有方法在超越传统聚合物范畴、利用多样化材料制备复杂三维结构方面仍面临挑战。
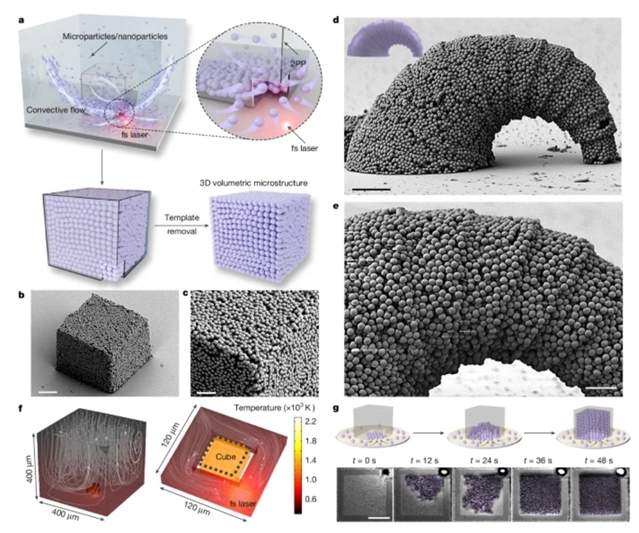
研究组提出一种普适性三维微纳加工策略,通过精准调控受限三维空间内的光流控相互作用,实现对多种材料的兼容性构筑,可制备具有空间自由形态的三维微纳结构。飞秒激光诱导的热点产生局域化热梯度,为负载纳米粒子的分散体系光流控相互作用提供精确时空调控。该技术能够将不同形态与组分(包括金属、金属氧化物、碳纳米材料及量子点等)的纳米粒子快速、高度局域化组装成复杂三维微结构。
为展示其多功能性,研究组制备了多种功能微型器件:例如具备尺寸选择性筛分功能的三维微流控阀门,可实现不同尺寸微米/纳米颗粒的快速分离;以及集成四种不同功能材料的微型机器人,通过不同外部刺激驱动实现多模态运动。这种光流控三维微纳加工方法为先进材料创新与微型器件开发开辟了新途径,将在胶体机器人学、微纳光子学、催化及微流控等领域展现广阔应用前景。
附:英文原文
Title: Optofluidic three-dimensional microfabrication and nanofabrication
Author: Lyu, Xianglong, Lei, Wenhai, Gardi, Gaurav, Khan, Muhammad Turab Ali, Bagheri, Shervin, Zhang, Mingchao, Sitti, Metin
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-28
Abstract: Three-dimensional (3D) microfabrication/nanofabrication technologies have revolutionized various fields by enabling the precise construction of complex microstructures/nanostructures1,2,3,4,5,6. However, existing methods face challenges in fabricating intricate 3D architectures from a diverse range of materials beyond conventional polymers. Here we introduce a universal 3D microfabrication/nanofabrication strategy compatible with a broad range of materials by precisely manipulating optofluidic interactions within a confined 3D space, enabling the creation of volumetric, free-form 3D microstructures/nanostructures. A femtosecond-laser-induced heating spot generates a localized thermal gradient, providing precise spatiotemporal control over optofluidic interactions of the nanoparticle-laden dispersions. This enables the rapid and highly localized assembly of nanoparticles with diverse shapes and compositions—including metals, metal oxides, carbon nanomaterials and quantum dots—into complex 3D microstructures. To demonstrate its versatility, we fabricate multifunctional microdevices, such as 3D microfluidic valves with size-selective sieving functionality, achieving fast separation of microparticles/nanoparticles with distinct dimensions, as well as microrobots integrated with four distinct functional materials, achieving multimodal locomotion powered by different external stimuli. This optofluidic 3D microfabrication/nanofabrication method unlocks new opportunities for advanced material innovation and miniaturized device development, paving the way for broad applications in colloidal robotics7, microphotonics/nanophotonics, catalysis and microfluidics.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-10033-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-10033-x
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
