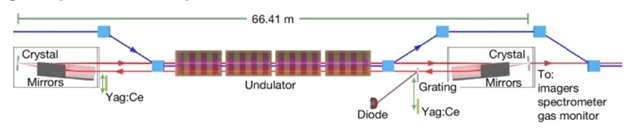
近日,德国电子同步加速器(DESY)公司Patrick Rauer团队研究了基于腔的X射线源的激光。相关论文于2026年1月28日发表在《自然》杂志上。
激光器的发明通过提供可见光波段的高强度相干光,彻底改变了光学领域,但将这一概念拓展至X射线波段,却因缺乏合适的增益介质和反射镜而受阻。当前硬X射线自由电子激光装置通过让高峰值电流电子束在长波荡器中单次通过并基于自放大自发辐射机制放大散粒噪声,实现了极高亮度,但其时域与光谱轮廓呈现多尖峰噪声特征。基于腔体的XFEL方案应运而生,通过使经过光谱滤波的X射线脉冲在布拉格反射腔内循环,并与高重复频率电子束同步,以期弥补这一缺陷。
研究组展示了在欧洲XFEL装置中,利用基于钻石的132.8米环形布拉格反射腔,在6.952千电子伏能级实现了与超导加速器2.23兆赫束团间隔匹配的多程增益激光发射。在严格的腔长稳定性与角度稳定性条件下,观测到腔内辐射通过连续束团实现逐束增幅的过程,并产生了微焦耳量级的高光谱纯度脉冲。这验证了基于腔体的XFEL在加速器环境中的可行性,同时证实了钻石布拉格光学元件在X射线谐振腔中的应用潜力。所实现的光谱纯度为新一代X射线科学开辟了道路——该领域迫切需要高度相干、高稳定度的光源。
附:英文原文
Title: Lasing of a cavity-based X-ray source
Author: Rauer, Patrick, Bahns, Immo, Friedrich, Bertram, Casalbuoni, Sara, Di Felice, Massimiliano, Dommach, Martin, Freijo Martin, Idoia, Freund, Wolfgang, Grnert, Jan, Guetg, Marc, Karpics, Ivars, Karabekyan, Suren, Koch, Andreas, Kujala, Naresh, La Civita, Daniele, Liu, Jia, Maltezopoulos, Theophilos, Makita, Mikako, Mayet, Frank, Mller, Lukas, Rio, Benoit, Samoylova, Liubov, Schmidtchen, Silja, Scholz, Matthias, Silenzi, Alessandro, Strauch, Vivienne, Thoden, Daniel, Wohlenberg, Torsten, Vannoni, Maurizio, Yang, Fan, Decking, Winfried, Rossbach, Joerg, Sinn, Harald
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-28
Abstract: The invention of the laser transformed optics by providing intense, coherent light in the visible region, but extending this concept to X-rays has been hindered by a lack of suitable gain media and mirrors. Current hard X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) facilities1,2,3,4,5 overcome this by amplifying shot noise from a high-peak-current electron bunch via self-amplified spontaneous emission6 in a single pass through long undulators, delivering very high brightness but with a noisy, multi-spiked temporal and spectral profile. Cavity-based XFELs (CBXFELs)7,8,9 were proposed to close this gap by recirculating spectrally filtered X-ray pulses in a Bragg-reflecting cavity synchronized to a high-repetition-rate electron beam. Here we show lasing with multi-pass gain at 6.952keV in a 132.8-m round-trip diamond-based Bragg cavity10 at the European XFEL, matched to the 2.23-MHz bunch spacing of the superconducting accelerator5. Under stringent length and angular stability requirements, a ring-up in the cavity across successive bunches was observed, producing spectrally pure, microjoule-level pulses. This establishes the feasibility of CBXFELs in an accelerator environment and validates diamond Bragg optics for X-ray resonators. The demonstrated spectral purity opens a path to next-generation X-ray science, which demands highly coherent, stable sources.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-10025-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-10025-x
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
