近日,中国科学院理化技术研究所吴骊珠团队报道了氧空位介导的异-不对称双活性位点打破了高效酸性水氧化的活性-稳定性权衡。相关论文于2026年1月27日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
调控反应路径以克服催化剂的活性-稳定性权衡难题在酸性析氧反应中至关重要,但仍极具挑战性。
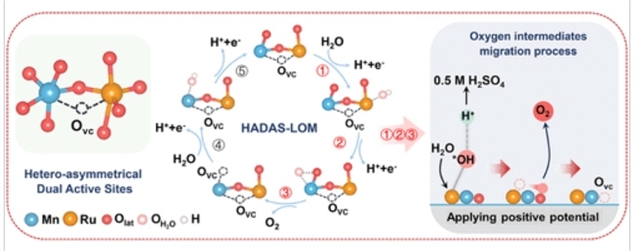
研究组通过水热反应、氩等离子体轰击与同构取代相结合的策略,将原子级分散的Ru引入富氧空位的MnO2-x主体中,构建了一种具有氧空位介导的异质不对称双活性位点Mn–Ovc–Ru单元的新型催化剂。该催化剂在0.5 M H2SO4中表现出卓越性能:在100 mA cm-2电流密度下过电位仅为233 mV,且在10 mA cm-2下可稳定运行超过5000小时。用于质子交换膜水电解槽时,仅需1.76 V电压即可达到3 A cm-2的电流密度(超越美国能源部2026年技术目标:1.8 V@3 A cm-2),并在1 A cm-2下稳定运行2200小时,电压衰减率仅为22.3 μV h-1,使其跻身顶级Ru/Ir基催化剂行列。
操作表征与理论计算表明,独特的Mn–Ovc–Ru单元中增强的Ru–O共价性与缩短的Ru–Mn距离,共同促成了异质不对称双活性位点辅助的晶格氧机制。在该机制中,O中间体从Ru位点转移至Mn位点,与晶格氧耦合实现快速O2释放。桥接的氧空位增加了Ru位点的电子密度以缓解过氧化,而Ru–Mn双位点的协同作用使得Mn周围的晶格氧(而非Ru周围的晶格氧)形成OO中间体,从而有效保护Ru免于溶解。这项工作为在酸性稳定高效析氧反应电催化剂设计中,构建氧空位与多重活性位点协同体系提供了新范式。
附:英文原文
Title: Oxygen Vacancy-Mediated Hetero-Asymmetrical Dual Active Sites Break the Activity-Stability Trade-Off for Efficient Acidic Water Oxidation
Author: Qiang Gao, Anquan Zhu, Guangzu Liu, Zhiyi Sun, Teng Li, Cui Xu, Xianjun Yin, Feng Li, Wenxing Chen, Zenghe Li, Li-Zhu Wu, Bin Liu
Issue&Volume: January 27, 2026
Abstract: Regulating the reaction pathway to overcome the activity-stability trade-off of catalysts is significant but remains highly challenging in acidic oxygen evolution reactions (OERs). Herein, we incorporated atomically dispersed Ru into an oxygen vacancy-rich (Ovc) MnO2–x host through a combination of hydrothermal reaction, argon-plasma bombardment, and isomorphic substitution, resulting in a distinctive catalyst (Ru-AP-MnO2–x) featuring Ovc-mediated heteroasymmetric dual-active-site Mn–Ovc–Ru units. Impressively, the Ru-AP-MnO2–x catalyst achieved a low overpotential of 233 mV at 100 mA cm–2 and demonstrated an exceptional stability for >5000 h at 10 mA cm–2 in 0.5 M H2SO4. When used in a proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer (PEMWE), it required a potential of only 1.76 V to reach 3 A cm–2 (surpassing the DOE 2026 target: 1.8 V at 3 A cm–2) and operated stably at 1 A cm–2 for up to 2200 h with an extremely low potential decay rate of only 22.3 μV h–1, positioning it among the top-ranked Ru/Ir-based catalysts. Operando characterizations and theoretical calculations demonstrated that enhanced Ru–O covalency and reduced Ru–Mn distance in the unique Mn–Ovc–Ru unit enabled a heteroasymmetrical-dual-active-site-assisted lattice oxygen mechanism (HADAS-LOM) for OER, where the *O intermediates transferred from Ru to Mn sites coupled lattice O (Olat) for rapid O2 release. Moreover, the bridged Ovc increased the electron density at Ru sites to mitigate overoxidation, while synergistic Ru–Mn dual sites allowed Olat around Mn instead of Ru sites to form an *OO intermediate, effectively protecting Ru from dissolution. This work offers a blueprint for engineering Ovc and multiple active-site synergy in the design of acid-stable, high-efficiency OER electrocatalysts.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09492
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c09492
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
