近日,武汉工程大学戴武斌团队报道了通过Li+和F-取代控制的局域电荷积累和氧空位工程同时调制ZnGa2O4中的锰价。2026年1月26日,《结构化学》杂志发表了这一成果。
锰激活荧光粉备受关注,但Mn4+不可避免的自还原为Mn2+过程以及Mn4+/Mn2+含量的精准调控仍是严峻挑战。
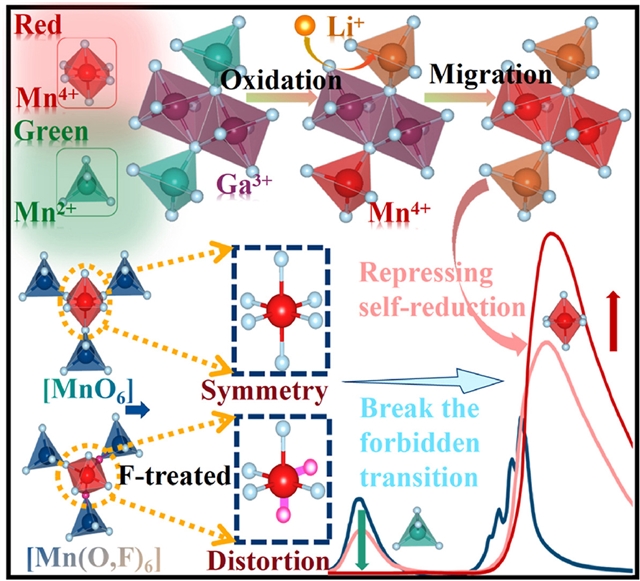
研究组通过在空气中进行固相反应证明,通过掺入Li+与F-,可在常规尖晶石结构的ZnGa2O4中精确调控自还原程度与锰的价态,实现按需设计的颜色可调光致发光——从蓝色自发光到Mn4+/Mn2+的红/绿发光。理论分析(包括密度泛函理论、键能理论)与实验研究(动态/静态光谱分析)均表明,占据四面体Zn2+位的Li+可将Mn4+推入八面体Ga3+位,并因其周围局域电荷聚集消耗过剩电子,从而抑制Mn4+的自还原。
此外,F-取代可修复本征氧空位,进一步抑制自还原及有害的电子捕获效应。同时,Li+/F-的引入能扭曲ZnGa2O4晶格、打破Mn4+的禁戒跃迁,从而拓宽发光谱带并提升效率。研究组还深入探讨了具有宽浅/深陷阱的ZnGa2O4:Mn/Li/F的长余辉发光特性。最终,该材料基于Li/F调控的可调光致发光与长余辉发光特性,在比率光学温度计、植物照明、白光LED及动态防伪等领域展现出巨大应用潜力。
附:英文原文
Title: Manganese valence modulation in ZnGa2O4 via simultaneously localized charge accumulation and oxygen vacancy engineering controlled by Li+ and F- substitutions for tailored applications
Author: anonymous
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-26
Abstract: Mn-activated phosphors have attracted great attention, but the inevitable self-reduction of Mn4+ to Mn2+ and precise regulation of Mn4+/Mn2+ content remain serious challenges. Herein, through solid-state reaction in air, we demonstrate that the degree of self-reduction and valence of Mn can be accurately manipulated in normal spinel ZnGa2O4 (ZGO) by incorporation of Li+ and F-, achieving color-tunable photoluminescence (PL) as desired, from blue self-luminescence to red/green emission of Mn4+/Mn2+. Both theoretical (i.e., density functional theory, bond energy theory) and experimental (i.e., dynamic/static spectroscopy) analyses indicate that Li+ occupying the tetrahedral Zn2+ site can push Mn4+ into the octahedral Ga3+ site and restrain self-reduction of Mn4+ owing to localized charge accumulation around Li+ that depletes excess electrons. Furthermore, F substitution can repair intrinsic oxygen vacancies, further suppressing self-reduction and detrimental electron-capturing effects. Meanwhile, Li+/F incorporation can distort ZGO and break the forbidden transition of Mn4+, leading to broadened PL and enhanced efficiency. The long-persistent PL (LPL) of ZGO: Mn/Li/F with wide shallow/deep traps is also explored in depth. Finally, the Li/F-dependent tunable PL and LPL of ZGO: Mn/Li/F show great potential for applications in ratiometric optical thermometers, plant lighting, white LEDs, and dynamic anticounterfeiting.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2026.100868
Source: https://cjsc.ac.cn/cms/issues/988
Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry:《结构化学》,创刊于1982年。隶属于中国结构化学杂志,最新IF:2.2
官方网址:http://cjsc.ac.cn/
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/cjschem/default2.aspx
