近日,南京大学马晶团队研究了基于DFT的机器学习流程映射抗生素光催化转化和耐药性风险。该项研究成果发表在2026年1月20日出版的《德国应用化学》杂志上。
光催化降解抗生素虽然高效,但可能产生维持甚至放大生态风险的转化产物,包括诱导抗生素抗性基因的生成。
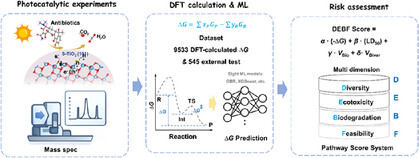
研究组开发了一个耦合光催化实验、高分辨质谱、密度泛函理论计算与机器学习的预测框架,用于评估转化产物的风险。以四环素为模型化合物,他们构建了包含120余步、9533个反应的反应网络,并训练出能以密度泛函理论精度快速预测吉布斯自由能变化的机器学习模型。通过集成自动过渡态搜索,评估了反应网络中的动力学可达性。该方法的普适性在包含545个反应的五种不同抗生素降解路径中得到验证。
此外,研究组建立了整合多样性、生态毒性、生物降解性与反应可行性的多维评分系统,以同时基于反应活性与可持续性对反应路径进行优先级排序。研究组发现若干羟基化、胺化及酰胺-酮类转化产物属于高风险物种,其抗生素抗性基因结合潜力显著增强。通过将分子能量学与生态效应相联结,这项工作为分析光催化转化过程提供了一种可推广、机理锚定且具备风险意识的系统方法,并为制定兼顾效率与生态安全的污染物降解设计原则提供了理论基础。
附:英文原文
Title: Mapping Antibiotic Photocatalytic Transformation and Resistance Risks with a DFT-Informed Machine Learning Workflow
Author: Chen-Chen Zhao, Sihan Xing, Cheng Fu, Lifeng Zheng, Huaizhu Wang, Zhong Jin, Shuhua Li, Shujuan Zhang, Jing Ma
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-20
Abstract: The photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics is effective but may yield transformation products (TPs) that sustain or amplify ecological risks, including antibiotic resistance gene (ARG) induction. This study developed a predictive framework that couples photocatalytic experiments, high-resolution mass spectrometry, density functional theory (DFT) calculations and machine learning (ML) to assess risks of TPs. Using tetracycline as a model compound, we constructed a reaction network over 120 steps and 9 533 reactions, and trained an ML model to rapidly predict Gibbs free energy changes with DFT accuracy. Automatic transition-state searches were integrated to evaluate kinetic accessibility within the network. The generalizability of this approach was validated with pathways of five different antibiotics involving 545 reactions. Furthermore, a multi-dimensional scoring system was developed that integrates diversity, ecotoxicity, biodegradability, and feasibility (DEBF) to prioritize pathways by both reactivity and sustainability. Several hydroxylated, aminated, and amide–ketone TPs were identified as high-risk species with enhanced ARG-binding potential. By bridging molecular energetics with ecological outcomes, this work offers a generalizable, mechanism-anchored, and risk-aware approach for analyzing photocatalytic transformations and deriving design principles for pollutant degradation that balance efficiency with ecological safety.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202520124
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202520124
Angewandte Chemie:《德国应用化学》,创刊于1887年。隶属于德国化学会,最新IF:16.823
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213773
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/anie/default.aspx
