约翰霍普金斯大学Gira Bhabha小组取得一项新突破。他们的最新研究揭示了LetA定义了一个结构上独特的转运蛋白家族。这一研究成果发表在2026年1月21日出版的国际学术期刊《自然》上。
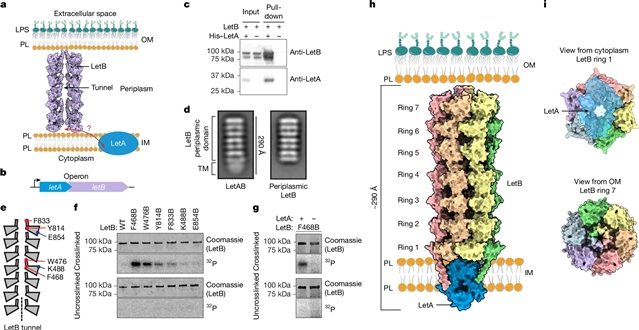
在这里,研究团队确定了大肠杆菌LetAB的结构,这是一种参与外膜完整性的磷脂转运蛋白,发现LetA采用了一种独特的结构,在结构和进化上与已知的转运蛋白家族无关。LetA定位于内膜,在那里它准备将脂质装载到它的结合伙伴LetB中,LetB是一种哺乳动物细胞进入(MCE)蛋白,形成大约225脂质通过细胞包膜运输的长通道。出乎意料的是,LetA跨膜结构域采用了一种与真核生物膜蛋白四跨蛋白家族进化相关的折叠,包括跨膜AMPA受体调节蛋白(TARPs)和claudins。通过深度突变扫描、分子动力学模拟、AlphaFold预测的替代状态和功能研究的结合,该课题组研究人员提出了一个leta样膜转运蛋白家族如何促进脂质在细菌细胞包膜上的运输的模型。
据了解,膜转运蛋白在细胞膜上转运各种各样的货物,从小糖到整个蛋白质。一些结构独特的蛋白质家族已经被描述,它们解释了大多数已知的膜运输过程。然而,许多具有预测转运蛋白功能的膜蛋白仍未被表征。
附:英文原文
Title: LetA defines a structurally distinct transporter family
Author: Santarossa, Cristina C., Li, Yupeng, Yousef, Sara, Hasdemir, Hale S., Rodriguez, Carlos C., Haase, Max A. B., Baek, Minkyung, Coudray, Nicolas, Pavek, John G., Focke, Kimber N., Silverberg, Annika L., Bautista, Carmelita, Yeh, Johannes T.-H., Marty, Michael T., Baker, David, Tajkhorshid, Emad, Ekiert, Damian C., Bhabha, Gira
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-21
Abstract: Membrane transport proteins translocate diverse cargos, ranging from small sugars to entire proteins, across cellular membranes1,2,3. A few structurally distinct protein families have been described that account for most of the known membrane transport processes4,5,6. However, many membrane proteins with predicted transporter functions remain uncharacterized. Here we determined the structure of Escherichia coli LetAB, a phospholipid transporter involved in outer membrane integrity, and found that LetA adopts a distinct architecture that is structurally and evolutionarily unrelated to known transporter families. LetA localizes to the inner membrane, where it is poised to load lipids into its binding partner, LetB, a mammalian cell entry (MCE) protein that forms an approximately 225 long tunnel for lipid transport across the cell envelope. Unexpectedly, the LetA transmembrane domains adopt a fold that is evolutionarily related to the eukaryotic tetraspanin family of membrane proteins, including transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins (TARPs) and claudins. Through a combination of deep mutational scanning, molecular dynamics simulations, AlphaFold-predicted alternative states and functional studies, we present a model for how the LetA-like family of membrane transporters facilitates the transport of lipids across the bacterial cell envelope.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09990-0
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09990-0
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
