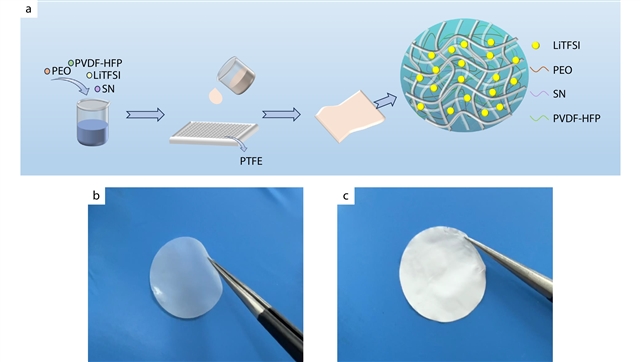
近日,浙江理工大学郭玉海团队报道了由丁二腈和聚四氟乙烯多孔纤维膜制备的锂金属电池用高离子导电、机械坚固的固体聚合物复合电解质。相关论文于2026年1月19日发表在《中国高分子科学杂志》上。
固体聚合物电解质因其易于制备及与锂金属的良好兼容性,被认为是全固态锂金属电池的理想候选材料。然而,其低离子电导率和较弱的力学性能限制了实际应用。
研究组制备了一种由聚环氧乙烷(PEO)、聚偏氟乙烯-六氟丙烯(PVDF-HFP)、增塑剂丁二腈(SN)以及聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)纤维多孔膜组成的复合固体聚合物电解质。其中PTFE纤维膜作为支撑骨架,显著增强了电解质的机械强度;SN降低了PEO的结晶区域,促进了锂离子的快速传输;PVDF-HFP则有助于锂盐的溶解并提升电解质的电化学稳定性。
优化后的PTFE/PEO/PVDF-HFP/SN聚合物电解质在352%的伸长率下拉伸强度达到3.31 MPa,并在60°C下实现7.6×10-4 S·cm-1的离子电导率。锂对称电池在0.15 mA·cm-2电流密度下稳定循环超过2500小时,Li//LiFePO4全电池在0.5 C倍率下循环300次后容量保持率达91.6%,且循环过程中库仑效率始终高于99.9%。
附:英文原文
Title: High Ionic Conductive, Mechanical Robust Solid Polymer Composite Electrolyte Achieved by Succinonitrile and Polytetrafluoroethylene Porous Fibrous Membrane for Lithium Metal Batteries
Author: Shuai-Jun Chen, Biao Huang, Li-Xin Song, Zha Wang, Ping-Fan Du, Jie Xiong, Hai-Lin Zhu, Yu-Hai Guo
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-19
Abstract: Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) are considered promising candidates for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries because of their easy preparation and good compatibility with lithium metal. However, their applications are restricted by their low ionic conductivity and poor mechanical properties. In this study, a composite solid polymer electrolyte composed of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP), plasticizer succinonitrile (SN), and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) fibrous porous membranes was prepared. The PTFE fibrous membrane significantly enhanced the mechanical strength of the electrolyte as a supporting framework. SN reduced the crystalline regions of PEO and facilitated rapid lithium-ion transport. PVDF-HFP promoted lithium salt dissolution and improved the electrochemical stability of the electrolyte. Accordingly, the optimized PTFE/PEO/PVDF-HFP/SN polymer electrolyte exhibited a tensile strength of 3.31 MPa at 352% elongation and demonstrated an ionic conductivity of 7.6×10–4 S·cm–1 at 60 °C. Lithium symmetric cells maintained stable cycling for over 2500 h at 0.15 mA·cm–2, and Li//LiFePO4 full cells showed a high capacity retention of 91.6% after 300 cycles at 0.5 C, with coulombic efficiency consistently exceeding 99.9% throughout cycling.
DOI: 10.1007/s10118-025-3515-3
Source: https://www.cjps.org/en/article/doi/10.1007/s10118-025-3515-3/
Chinese Journal of Polymer Science:《中国高分子科学杂志》,创刊于1983年。隶属于中国化学会,最新IF:4.3
官方网址:https://www.cjps.org/
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjps
