近日,英国伦敦大学学院Wei Zhang团队报道了催化激发的d波段中心工程实现氢抑制锌阳极用于长寿命水性锌离子电池。相关论文于2026年1月19日发表在《科学通报》杂志上。
水系锌离子电池因其储能潜力备受关注,但锌负极的不稳定性——主要源于枝晶生长、析氢反应及副产物形成——限制了其实际应用。其中,析氢反应会加速锌的消耗、破坏电极结构完整性并引发局部碱化,进而加剧钝化问题。传统策略侧重于电解液配方优化与表面钝化,却较少触及锌表面析氢反应的电子本质。
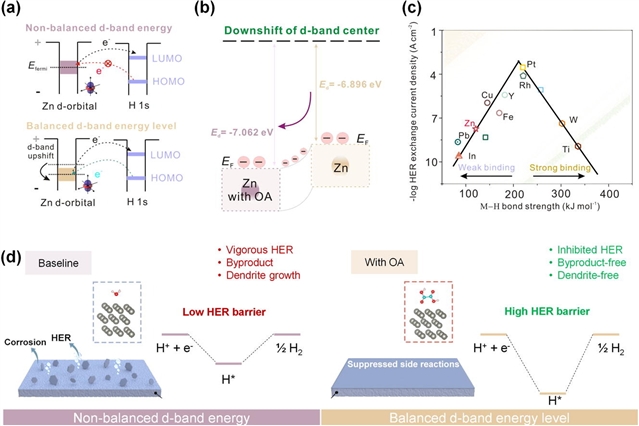
研究组报道了一种受催化启发的策略,通过d带中心调控从电子层面调节锌的反应活性,从而从本质上抑制析氢反应。通过引入草酸作为分子添加剂,他们实现了锌d带中心的显著下移(从-6.896 eV降至-7.062 eV),削弱了氢吸附作用,从根本上降低了析氢活性。同时,草酸通过取代配位的硫酸根阴离子,破坏了锌离子的溶剂化结构,从而抑制了界面副产物的生成。
这种双重效应带来了前所未有的性能表现:锌对称电池稳定运行超过3500小时;锌铜电池在1500次循环中库仑效率达99.41%;锌碘电池在10000次循环后容量保持率达92.8%;1.3安时的锌碘软包电池也展现出良好的循环性能。该研究开创了电池设计中表面电子调控的新范式,将催化d带理论拓展至电化学界面,为抑制水系金属电池的析氢反应和稳定界面提供了新思路。
附:英文原文
Title: Catalysis-inspired d-band center engineering enables hydrogen-suppressed zinc anodes for long-life aqueous zinc-ion batteries
Author: Qingjin Fu f, Nana Xu g, Wei Zhang b
Issue&Volume: 2026/01/19
Abstract: Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) are promising for energy storage. However, Zn anode instability—caused by dendrite growth, hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and by-product formation—limits their practical viability. HER, in particular, accelerates Zn consumption, disrupts electrode integrity, and induces local alkalization, exacerbating passivation. Conventional strategies emphasize electrolyte formulation and surface passivation, yet few address the underlying electronic origin of HER on Zn. Here we report a catalysis-inspired strategy that electronically modulates Zn reactivity via d-band center engineering to intrinsically suppress HER. By introducing oxalic acid (OA) as a molecular additive, we achieve a significant downward shift in the Zn d-band center (from –6.896 to –7.062 eV), weakening hydrogen adsorption and fundamentally reducing HER activity. In parallel, OA disrupts the Zn2+ solvation structure by displacing coordinated SO2– 4 anions, suppressing interfacial by-product formation. These dual effects yield unprecedented performance: Zn||Zn symmetric cells operate stably for over 3500 h; Zn||Cu cells exhibit 99.41% Coulombic efficiency over 1500 cycles; and Zn||I2 cell retain 92.8% capacity after 10,000 cycles; the 1.3 Ah Zn||I2 pouch cell presents good cyclability. This work pioneers a surface electronic tuning paradigm in battery design, extending catalytic d-band theory to electrochemical interfaces for HER suppression and interfacial stabilization in aqueous metal batteries.
DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2026.01.033
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S209592732600040X
Science Bulletin:《科学通报》,创刊于1950年。隶属于SciEngine出版平台,最新IF:18.9
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SB/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/csb
