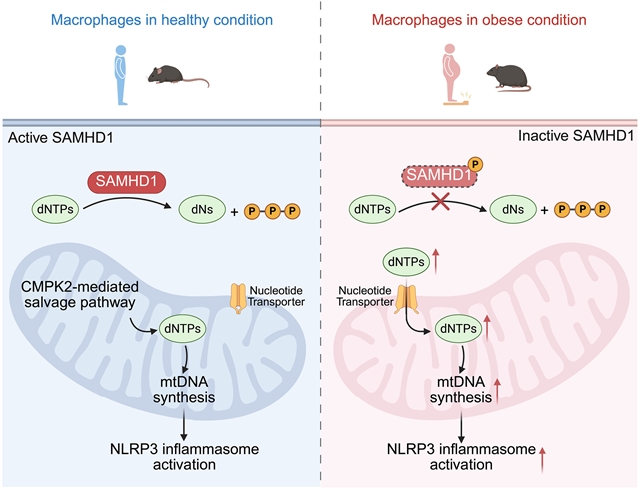
小组发现,肥胖通过破坏SAM和HD结构域蛋白1 (SAMHD1)(一种对核苷酸平衡至关重要的脱氧核苷三磷酸(dNTP)水解酶),诱导巨噬细胞中含有Nod样受体pyrin结构域3(NLRP3)的炎性体过度激活和过量的白细胞介素(IL) -1β的产生。这导致dNTPs的异常积累,这些dNTPs可以被运输到线粒体中,并启动线粒体DNA (mtDNA)的新合成,从而增加氧化mtDNA的存在并引发NLRP3的过度激活。在斑马鱼、小鼠和人类分离的细胞中,SAMHD1的缺失促进了NLRP3的过度激活。SAMHD1缺陷小鼠表现出循环IL-1β升高、胰岛素抵抗和代谢功能障碍相关的脂肪性肝炎。阻断dNTP线粒体运输可阻止肥胖患者和SAMHD1缺陷小鼠巨噬细胞中NLRP3的过度激活。他们的研究表明,肥胖通过抑制SAMHD1重新连接巨噬细胞核苷酸代谢,从而引发NLRP3炎性体过度激活,从而推动疾病进展。
据悉,肥胖是一个主要的疾病危险因素,由于肥胖相关的过度炎症。
附:英文原文
Title: Nucleotide metabolic rewiring enables NLRP3 inflammasome hyperactivation in obesity
Author: Danhui Liu, Chuanli Zhou, Xiaochen Wang, Zhou Luo, Ruiyao Xu, Shanshan Huo, Lina Guo, Xuemei Luo, Shuhan Yang, Arielle Click, Janiece Vancil, Paola Barajas, Victor Mijares, Hamid Baniasadi, Nan Yan, Jan Rehwinkel, Dustin C. Hancks, Elizabeth H. Chen, Shuang Liang, Zhenyu Zhong
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-15
Abstract: Obesity is a major disease risk factor due to obesity-associated hyperinflammation. We found that obesity induced Nod-like receptor pyrin domain–containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome hyperactivation and excessive interleukin (IL)–1β production in macrophages by disrupting SAM and HD domain–containing protein 1 (SAMHD1), a deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) hydrolase crucial for nucleotide balance. This caused aberrant accumulation of dNTPs, which can be transported into mitochondria, and initiated mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) neosynthesis, which increased the presence of oxidized mtDNA and triggered NLRP3 hyperactivation. Deletion of SAMHD1 promoted NLRP3 hyperactivation in cells isolated from zebrafish, mice, and humans. SAMHD1-deficient mice showed elevated circulating IL-1β, insulin resistance, and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis. Blocking dNTP mitochondrial transport prevented NLRP3 hyperactivation in macrophages from obese patients and SAMHD1-deficient mice. Our study revealed that obesity by inhibiting SAMHD1 rewired macrophage nucleotide metabolism, thereby triggering NLRP3 inflammasome hyperactivation to drive disease progression.
DOI: adq9006
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adq9006
