泛素连接酶KLHL6驱动CD8+ T细胞功能障碍的抗性,这一成果由中国医学科学院李贵登团队经过不懈努力而取得。2026年1月14日,国际知名学术期刊《自然》发表了这一成果。
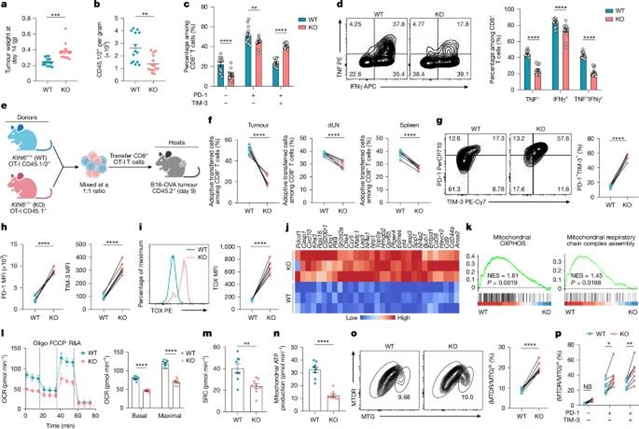
在这里,该课题组研究人员将T细胞衰竭和线粒体适应度图谱的计算分析与靶向的体内CRISPR筛选相结合,发现E3泛素连接酶KLHL6是T细胞衰竭和线粒体功能障碍的双负调节因子。在机制上,KLHL6的表达促进了TOX多泛素化和随后的蛋白酶体降解,从而减弱了祖细胞衰竭的T细胞向终末衰竭的转变。同时,KLHL6通过PGAM5-Drp1轴的翻译后调控,抑制慢性T细胞受体刺激过程中发生的过度线粒体分裂,从而维持线粒体适应性。
然而,KLHL6被T细胞受体连接自然下调,在暴露于慢性刺激时降低其潜在有益的泛素连接酶活性。在T细胞中增强KLHL6的表达可显著提高抗肿瘤和体内病毒感染的疗效和长期持久性。这些发现揭示了KLHL6是一个多功能的、临床可操作的癌症免疫治疗靶点,并强调了调节蛋白质平衡和泛素修饰以改善免疫治疗的潜力。
研究人员表示,肿瘤浸润性T细胞的多方面功能障碍,包括衰竭和线粒体功能障碍,仍然是癌症免疫治疗的主要障碍。转录组学和表观基因组学对T细胞功能障碍的调控已经得到了广泛的研究,但蛋白质停滞在调节这些障碍中的作用仍然不太明确。
附:英文原文
Title: The ubiquitin ligase KLHL6 drives resistance to CD8+ T cell dysfunction
Author: Cheng, Hongcheng, Su, Yapeng, Pan, Xiaoli, Xu, Yue, Xie, Ermei, Du, Jing, Chen, Daniel G., Dai, Xiaomeng, Gottardo, Raphael, Greenberg, Philip D., Li, Guideng
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-14
Abstract: The multifaceted dysfunction of tumour-infiltrating T cells, including exhaustion and mitochondrial dysfunction, remains a major obstacle in cancer immunotherapy1,2,3,4,5,6. Transcriptomic and epigenomic regulation of T cell dysfunction have been extensively studied7,8,9, but the role of proteostasis in regulating these obstacles remains less defined. Here we combined computational analyses of atlases of T cell exhaustion and mitochondrial fitness with performed targeted in vivo CRISPR screens, which identified the E3 ubiquitin ligase KLHL6 as a dual-negative regulator of both T cell exhaustion and mitochondrial dysfunction. Mechanistically, KLHL6 expression promoted TOX poly-ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation, thereby attenuating the transition of progenitor exhausted T cells towards terminal exhaustion. Simultaneously, KLHL6 maintained mitochondrial fitness by constraining the excessive mitochondrial fission that occurs during chronic T cell receptor stimulation by means of post-translational regulation of the PGAM5–Drp1 axis. However, KLHL6 is naturally downregulated by T cell receptor ligation, mitigating its potentially beneficial ubiquitin ligase activities during exposure to chronic stimulation. Enforcing KLHL6 expression in T cells markedly improved efficacy and long-term persistence against tumours and during viral infections in vivo. These findings uncover KLHL6 as a multifunctional, clinically actionable target for cancer immunotherapy, and highlight the potential of modulating proteostasis and ubiquitin modification to improve immunotherapy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09926-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09926-8
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
