杜克大学David R. Sherwood团队宣布他们提出了卵母细胞向受精卵过渡时的程序性自噬促进谱系耐受性。相关论文于2026年1月12日发表在《自然—细胞生物学》杂志上。
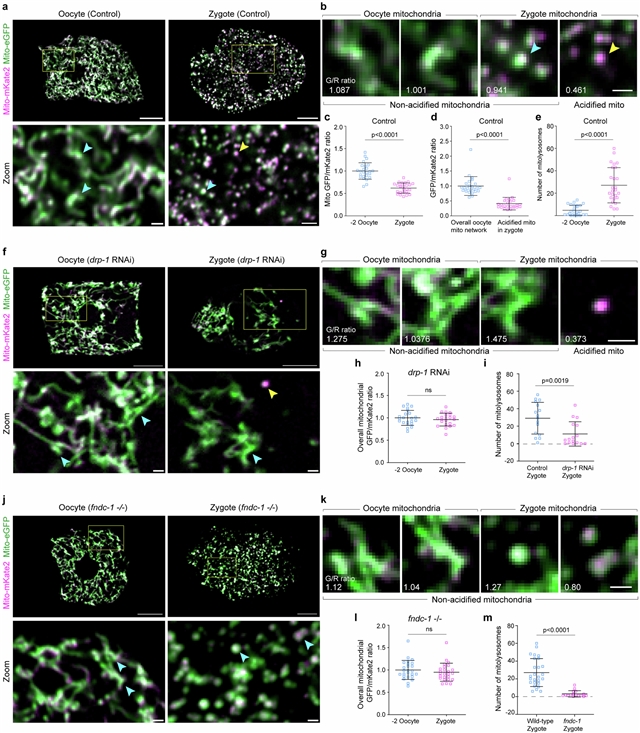
课题组在杆状体炎中发现在线虫发育过程中,卵母细胞向受精卵转变的开始触发了一个快速的有丝分裂事件。研究团队发现卵母细胞到受精卵的线粒体自噬(MOZT)需要线粒体断裂、巨噬途径和线粒体自噬受体FUNDC1,但不需要流行的线粒体自噬因子PINK1和BNIP3。MOZT减少了有害线粒体DNA的传播,从而保护了胚胎的存活。受损的MOZT驱动mtDNA突变在代际间的积累增加,导致后代种群的灭绝。因此,MOZT代表了一种在母婴传播过程中保持线粒体健康和保障谱系连续性的策略。
据介绍,从卵母细胞遗传的线粒体的质量决定了胚胎的生存能力、后代的终生代谢健康和谱系的持久性。高水平的内源性活性氧和外源性毒物对完全发育的卵母细胞的线粒体DNA (mtDNA)构成威胁。在成熟卵母细胞中通常检测到Deleteriothem mtDNA,但在胚胎中不存在,这表明存在一种隐式纯化选择机制。
附:英文原文
Title: Programmed mitophagy at the oocyte-to-zygote transition promotes lineage endurance
Author: Thendral, Siddharthan B., Bacot, Sasha, Ryde, Ian T., Morton, Katherine S., Chi, Qiuyi, Kenny-Ganzert, Isabel W., Meyer, Joel N., Sherwood, David R.
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-12
Abstract: The quality of mitochondria inherited from the oocyte determines embryonic viability, lifelong metabolic health of the progeny and lineage endurance. High levels of endogenous reactive oxygen species and exogenous toxicants pose threats to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in fully developed oocytes. Deleterious mtDNA is commonly detected in mature oocytes, but is absent in embryos, suggesting the existence of a cryptic purifying selection mechanism. Here, we discover that in Caenorhabditiselegans, the onset of oocyte-to-zygote transition developmentally triggers a rapid mitophagy event. We show that mitophagy at oocyte-to-zygote transition (MOZT) requires mitochondrial fragmentation, the macroautophagy pathway and the mitophagy receptor FUNDC1, but not the prevalent mitophagy factors PINK1 and BNIP3. MOZT reduces the transmission of deleterious mtDNA and as a result, protects embryonic survival. Impaired MOZT drives the increased accumulation of mtDNA mutations across generations, leading to the extinction of descendant populations. Thus, MOZT represents a strategy that preserves mitochondrial health during the mother-to-offspring transmission and safeguards lineage continuity.
DOI: 10.1038/s41556-025-01854-z
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41556-025-01854-z
Nature Cell Biology:《自然—细胞生物学》,创刊于1999年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.213
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ncb/
投稿链接:https://mts-ncb.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
