亥姆霍兹RNA感染研究所Chase L. Beisel研究小组近日取得一项新成果。经过不懈努力,他们揭示了靶向DNA ADP核糖基化触发细菌的模板修复和真核生物的碱基突变。2025年9月4日出版的《自然—生物技术》杂志发表了这项成果。
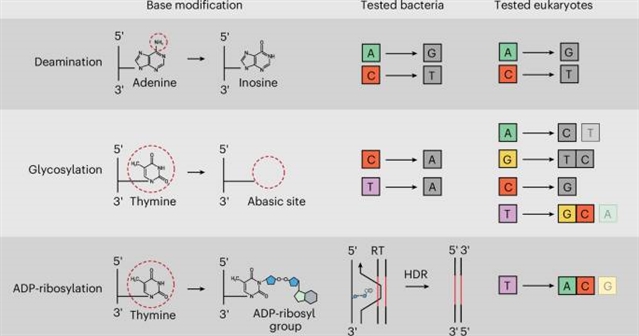
在这里,该课题组人员利用细菌抗噬菌体毒素DarT2将ADP-核糖基片段附加到DNA上,解锁细菌与真核生物不同的编辑结果。通过将减弱的DarT2修饰为Cas9缺失酶,课题组在靶DNA序列中编程胸腺嘧啶的位点特异性ADP核糖基化。在测试的细菌中,靶向驱动同源重组,提供灵活和无疤痕的基因组编辑,而不需要碱基替换或反选择。在测试的酵母,植物和人类细胞中,靶向驱动修饰的胸腺嘧啶取代腺嘌呤或腺嘌呤和胞嘧啶的混合物,并有有限的插入或删除,提供当前碱基编辑器无法实现的编辑。总的来说,他们的方法被称为追加编辑,利用向DNA中添加化学部分来扩展当前精确基因编辑的模式。
据介绍,碱基编辑器通过指导核碱基脱氨或去除而不诱导双链DNA断裂来创建精确的基因组编辑。然而,其他DNA修饰的巨大化学空间仍有待探索,以用于基因组编辑。
附:英文原文
Title: Targeted DNA ADP-ribosylation triggers templated repair in bacteria and base mutagenesis in eukaryotes
Author: Gupta, Darshana, Patinios, Constantinos, Bassett, Harris V., Kibe, Anuja, Collins, Scott P., Kamm, Charlotte, Wang, Yanyan, Zhao, Chengsong, Vollen, Katie, Toussaint, Christophe, Calvin, Irene, Cullot, Grgoire, Aird, Eric J., Polkoff, Kathryn M., Nguyen-Vo, Thuan Phu, Migur, Angela, Schut, Friso, AlAbri, Ibrahim S., Achmedov, Tatjana, Del Re, Alessandro, Corn, Jacob E., Saliba, Antoine-Emmanuel, Crook, Nathan, Stepanova, Anna N., Alonso, Jose M., Beisel, Chase L.
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-04
Abstract: Base editors create precise genomic edits by directing nucleobase deamination or removal without inducing double-stranded DNA breaks. However, a vast chemical space of other DNA modifications remains to be explored for genome editing. Here we harness the bacterial antiphage toxin DarT2 to append ADP-ribosyl moieties to DNA, unlocking distinct editing outcomes in bacteria versus eukaryotes. Fusing an attenuated DarT2 to a Cas9 nickase, we program site-specific ADP-ribosylation of thymines within a target DNA sequence. In tested bacteria, targeting drives homologous recombination, offering flexible and scar-free genome editing without base replacement or counterselection. In tested yeast, plant and human cells, targeting drives substitution of the modified thymine to adenine or a mixture of adenine and cytosine with limited insertions or deletions, offering edits inaccessible to current base editors. Altogether, our approach, called append editing, leverages the addition of chemical moieties to DNA to expand current modalities for precision gene editing.
DOI: 10.1038/s41587-025-02802-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-025-02802-w
Nature Biotechnology:《自然—生物技术》,创刊于1996年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:68.164
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nbt/
投稿链接:https://mts-nbt.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
