近日,中国科学技术大学孙道远团队实现了火星600公里固体内核的地震探测。相关论文发表在2025年9月3日出版的《自然》杂志上。
对于岩石行星,固体内核的存在对内核的组成和热演化以及行星的磁史具有显著的意义。在火星上,地球物理观测已经证实,地核至少部分是液态的,但尚不清楚地核是否有固态的。
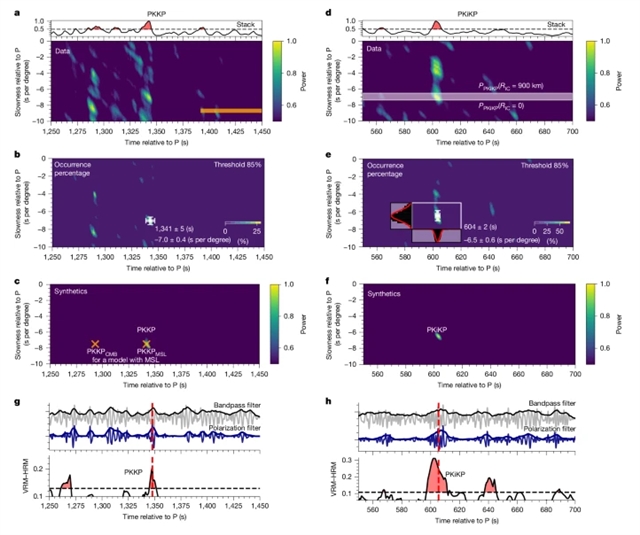
研究组展示了对洞察号任务获得的地震数据的分析,证明火星有一个坚实的内核。该团队确定了两个地震相,即深核过渡相PKKP和内核边界反射相PKiKP,揭示了内核。它们的倒转将火星内核的半径限制在大约613±67Km,纵波速度在内核边界上跳跃了约30%,并得到了额外的内核相关地震相的支持。这些性质意味着不同的轻元素集中在内核中,通过内核结晶与外核分离。这一发现为了解火星的热化学状态提供了一个定位点。此外,内核形成与火星磁场演化之间的关系可以为跨行星体的发电机产生提供见解。
附:英文原文
Title: Seismic detection of a 600-km solid inner core in Mars
Author: Bi, Huixing, Sun, Daoyuan, Sun, Ningyu, Mao, Zhu, Dai, Mingwei, Hemingway, Douglas
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-03
Abstract: For rocky planets, the presence of a solid inner core has notable implications on the composition and thermal evolution of the core and on the magnetic history of the planet1,2,3. On Mars, geophysical observations have confirmed that the core is at least partially liquid4,5,6,7, but it is unknown whether any part of the core is solid. Here we present an analysis of seismic data acquired by the InSight mission, demonstrating that Mars has a solid inner core. We identify two seismic phases, the deep core-transiting phase, PKKP, and the inner core boundary reflecting phase, PKiKP, indicative of the inner core. Our inversions constrain the radius of the Martian inner core to about 613±67km, with a compressional velocity jump of around 30% across the inner core boundary, supported by additional inner-core-related seismic phases. These properties imply a concentration of distinct light elements in the inner core, segregated from the outer core through core crystallization. This finding provides an anchor point for understanding the thermal and chemical state of Mars. Moreover, the relationship between inner core formation and the Martian magnetic field evolution could provide insights into dynamo generation across planetary bodies.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09361-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09361-9
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
