近日,意大利米兰理工大学Emanuele Sacchi团队研究了用于光子电路动态自配置的集成电子控制器。2025年9月30日,《光:科学与应用》杂志发表了这一成果。
可重构光子集成电路(PICs)可以直接在光域中实现任意操作和信号处理功能。这些电路的运行时配置需要一个电子控制层来调整其构建元件的工作点,并补偿输入信号的热漂移或退化。随着光子晶圆厂的进展,制造越来越复杂的芯片成为可能,开发可扩展的电子控制器对于复杂PICs的操作变得至关重要。
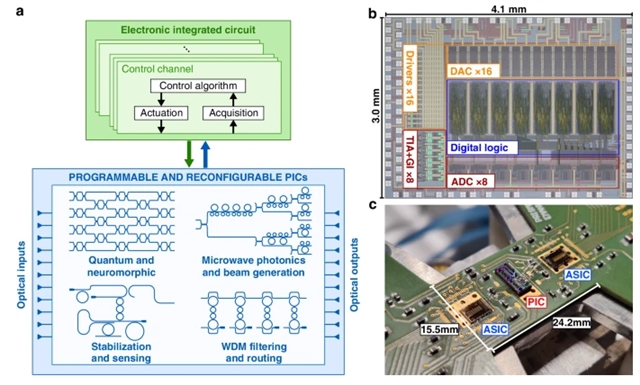
研究组提出了一种电子专用集成电路(ASIC),设计用于具有多个可调谐元件的PIC的重新配置。ASIC控制器的每个通道独立地处理PIC的一个光学元件,并操作多个并行的本地反馈回路以实现完全控制。通过对16通道硅光子自适应通用光束耦合器的实时重构,研究组验证了所提出的设计。结果证明了任意输入光束与单模波导的自动耦合,光束波前畸变的动态补偿以及通过光自由空间链路成功传输50 Gbit/s信号。低功耗和紧凑的电子芯片提供了一个可扩展的范例,可以无缝扩展到更大的光子架构。
附:英文原文
Title: Integrated electronic controller for dynamic self-configuration of photonic circuits
Author: Sacchi, Emanuele, Zanetto, Francesco, Martinez, Andres Ivan, SeyedinNavadeh, SeyedMohammad, Morichetti, Francesco, Melloni, Andrea, Sampietro, Marco, Ferrari, Giorgio
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-30
Abstract: Reconfigurable photonic integrated circuits (PICs) can implement arbitrary operations and signal processing functionalities directly in the optical domain. Run-time configuration of these circuits requires an electronic control layer to adjust the working point of their building elements and compensate for thermal drifts or degradations of the input signal. As the advancement of photonic foundries enables the fabrication of chips of increasing complexity, developing scalable electronic controllers becomes crucial for the operation of complex PICs. In this paper, we present an electronic application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) designed for reconfiguration of PICs featuring numerous tunable elements. Each channel of the ASIC controller independently addresses one optical component of the PIC, and multiple parallel local feedback loops are operated to achieve full control. The proposed design is validated through real-time reconfiguration of a 16-channel silicon photonics adaptive universal beam coupler. Results demonstrate automatic coupling of an arbitrary input beam to a single-mode waveguide, dynamic compensation of beam wavefront distortions and successful transmission of a 50 Gbit/s signal through an optical free-space link. The low power consumption and compactness of the electronic chip provide a scalable paradigm that can be seamlessly extended to larger photonic architectures.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01977-w
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01977-w
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
