中山大学于君团队宣布他们揭示了乳杆菌通过与肝细胞结合并产生喹啉酸促进肝细胞癌变。相关论文于2025年9月25日发表在《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
该课题组发现Catenibacterium在HCC患者的粪便和肿瘤中都富集。C. mitsuokai在常规小鼠和无菌小鼠中加速HCC癌变。
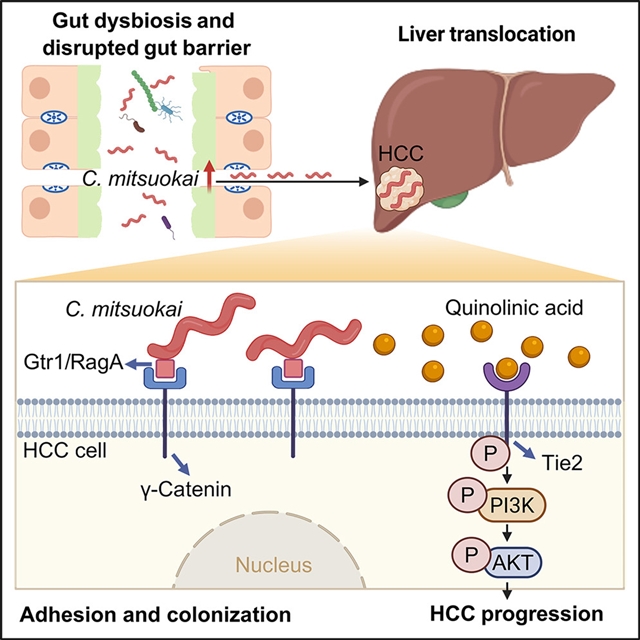
此外,C. mitsuokai破坏了肠道屏障,并作为活细菌转移到肝脏。重要的是,C. mitsuokai表面蛋白Gtr1/RagA与HCC细胞上的γ-连环蛋白受体相互作用,促进其在母细胞肝脏中的附着和定植。课题组进一步发现,C. mitsuokai的促肿瘤作用取决于其分泌的代谢物喹啉酸。在机制上,喹啉酸结合并激活肝癌细胞上具有免疫球蛋白和表皮生长因子同源结构域2 (TIE2)的酪氨酸激酶。磷酸化的TIE2随后激活下游致癌磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B (PI3K/AKT)通路,从而促进HCC进展。综上所述,C. mitsuokai破坏肠道屏障,通过Gtr1/RagA-γ-catenin定植HCC细胞,分泌喹啉酸,与TIE2结合,驱动PI3K/AKT通路,促进HCC的发展。
研究人员表示,肠道微生物在肝细胞癌(HCC)发病机制中的作用尚不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Catenibacterium mitsuokai promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by binding to hepatocytes and generating quinolinic acid
Author: Ying Zhang, Weixin Liu, Chi Chun Wong, Qian Song, Xinyue Zhang, Qianying Zhou, Xuxin Ren, Xiaoxue Ren, Ruiyan Xuan, Yutong Zhao, Linfu Xu, Xiaoxing Li, Lixia Xu, Xiang Zhang, Ming Kuang, Jun Yu
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-25
Abstract: The role of gut microbes in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. Here, we identified that Catenibacterium is enriched in both the feces and tumors of patients with HCC. C. mitsuokai accelerated HCC carcinogenesis in both conventional and germ-free mice. Furthermore, C. mitsuokai disrupted the gut barrier and translocated to the liver as live bacteria. Critically, the C. mitsuokai surface protein Gtr1/RagA interacts with the γ-catenin receptor on HCC cells, facilitating its attachment and colonization in the mouse liver. We further revealed that the pro-tumorigenic effect of C. mitsuokai depends on its secreted metabolite, quinolinic acid. Mechanistically, quinolinic acid binds to and activates the tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin and epidermal growth factor homology domains 2 (TIE2) on HCC cells. Phosphorylated TIE2 subsequently activates the downstream oncogenic phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathway, thereby promoting HCC progression. In summary, C. mitsuokai disrupts the gut barrier, colonizes HCC cells via Gtr1/RagA-γ-catenin, and secretes quinolinic acid, which binds to TIE2 and drives the PI3K/AKT pathway to promote HCC development.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.09.001
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00386-9
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
