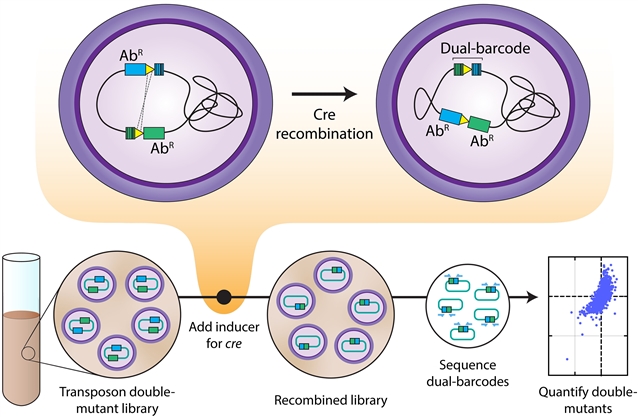
该课题组报道了双转座子测序(dual Tn-seq),这是一个平行分析综合双突变体库适应度的平台。使用Cre-lox系统进行双Tn-seq偶对随机条形码转座子位点测序,能够对肺炎链球菌130万个可能双基因缺失中的73%进行深度采样。发现的遗传相互作用跨越了广泛的生化过程,揭示了可能已经得到充分研究的途径中的新因素,例如胞苷三磷酸合成酶PyrJ。
此外,这种方法应该允许进一步研究生长条件特异性遗传相互作用。由于双Tn-seq不需要构建大量的单一突变体,因此它应该很容易适应各种微生物。
据了解,基因冗余使基因功能的系统表征复杂化,因为单基因缺失可能不会产生可识别的表型。
附:英文原文
Title: Dual transposon sequencing profiles the genetic interaction landscape in bacteria
Author: Justin J. Zik, Morgan N. Price, Keisha Hanifa Alma Mayra, Audrey A. Santoso, Adam P. Arkin, Adam M. Deutschbauer, Lok-To Sham
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-25
Abstract: Gene redundancy complicates systematic characterization of gene function as single-gene deletions may not produce discernible phenotypes. We report dual transposon sequencing (dual Tn-seq), a platform for assaying the fitness of a comprehensive double mutant pool in parallel. Dual Tn-seq couples random barcode transposon site sequencing with the Cre-lox system, enabling deep sampling of 73% of the 1.3 million possible double gene deletions in Streptococcus pneumoniae. The genetic interactions identified span a wide range of biochemical processes, revealing new factors in presumably well-studied pathways, exemplified by a cytidine triphosphate synthase PyrJ. Moreover, this approach should permit further investigation of growth condition–specific genetic interactions. Because dual Tn-seq does not require the construction of a large array of single mutants, it should be readily adaptable to various microorganisms.
DOI: adt7685
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adt7685
