近日,捷克查尔斯大学Kozk, Martin团队研究了光基电子像差校正器。2025年9月23日,《自然—光子学》杂志发表了这一成果。
在电子显微镜中实现原子分辨率历来受到球面像差的阻碍,这是传统电子透镜的一个基本限制。它的修正通常需要复杂的电磁多极组合。
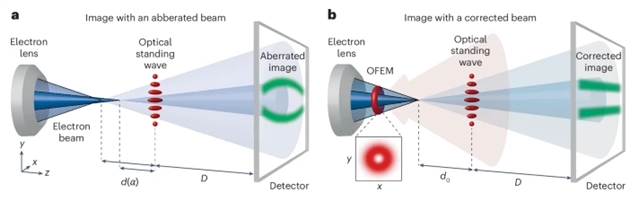
研究组证明了圆柱对称电子透镜的三阶球像差,其相关像差系数为Cs≈2.5M,可以通过与形光场的相互作用补偿到接近零。通过分析高倍率光驻波点投影电子像的畸变,量化了光致校正前后的球差。利用光质动势诱导电子的横向偏转,在原位超快四维扫描透射电子显微镜上精确表征了校正光场的空间分布。这种结合表征和校正的方法为电子束的光学控制引入了一种新的范例,并为高分辨率电子显微镜的紧凑可调光基校正器开辟了一条途径。
附:英文原文
Title: Light-based electron aberration corrector
Author: Chirita Mihaila, Marius Constantin, Koutensk, Petr, Moriov, Kamila, Kozk, Martin
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-23
Abstract: Achieving atomic resolution in electron microscopy has historically been hindered by spherical aberration, a fundamental limitation of conventional electron lenses. Its correction typically requires complex assemblies of electromagnetic multipoles. Here we demonstrate that third-order spherical aberration in a cylindrically symmetric electron lens with an associated aberration coefficient of Cs≈2.5m can be compensated to near-zero via interaction with a shaped light field. By analysing distortions in the high-magnification point-projection electron images of optical standing waves, we quantify the spherical aberration before and after light-induced correction. The spatial distribution of the correction optical field is precisely characterized in situ using ultrafast four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy utilizing the transverse deflection of electrons induced by the optical ponderomotive force. Such a combined characterization and correction approach introduces a new paradigm for optical control in electron beams and opens a pathway towards compact and tunable light-based correctors for high-resolution electron microscopy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01760-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-025-01760-8
