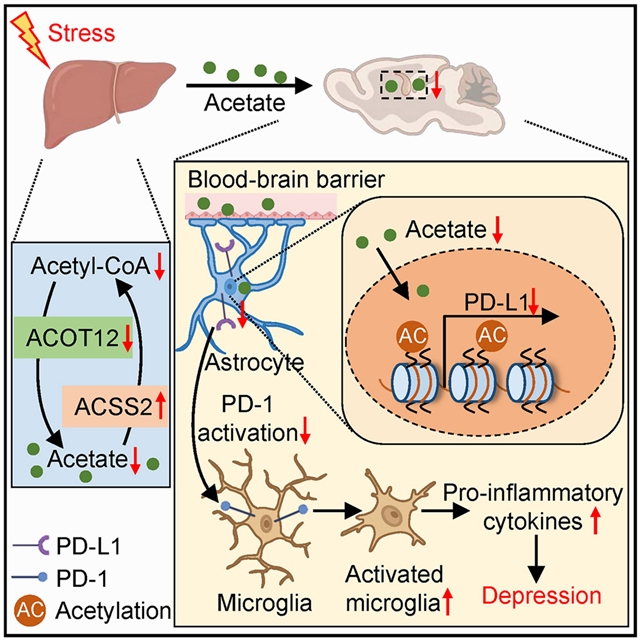
肝脏乙酰辅酶A代谢通过乙酸调节神经炎症和抑郁易感性,这一成果由华中科技大学陈建国研究组经过不懈努力而取得。2025年9月23日出版的《细胞—代谢》杂志发表了这项成果。
肝脏是代谢中枢,在这里小组证明了乙酰辅酶A的肝脏水解,一种中心代谢中间体,向大脑发出信号并帮助缓冲压力。利用雄性小鼠的慢性社会失败应激模式,课题组人员观察到肝脏葡萄糖到醋酸盐的代谢转换,随后是糖皮质激素抑制乙酰辅酶A水解酶、乙酰辅酶A硫酯酶12的转录,从而导致应激易感性。肝脏过表达乙酰辅酶A硫酯酶12通过增加乙酸输出促进腹侧海马组蛋白乙酰化,从而减轻抑郁样表型,从而增强星形胶质细胞中程序性细胞死亡配体1的表达,限制神经炎症并挽救抑制性突触传递功能障碍。他们的研究结果表明,肝乙酰辅酶A水解是调节抑郁易感性的关键肝脑轴成分。
研究人员表示,广泛的研究强调了神经精神疾病中受损的大脑能量代谢,而对外周代谢状态的作用知之甚少。
附:英文原文
Title: Hepatic acetyl-CoA metabolism modulates neuroinflammation and depression susceptibility via acetate
Author: Yu Cao, Yang Zhao, Tan Deng, Qigang Zhou, Gang Hu, Zhuang-Li Hu, Yan-Yi Jiang, Xiao-Han Yang, Fang Wang, Peng-Fei Wu, Jian-Guo Chen
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-23
Abstract: Extensive research highlights impaired brain energy metabolism in neuropsychiatric disorders, whereas much less is known about the role of the peripheral metabolic state. The liver is the metabolic hub, and herein we demonstrate that hepatic hydrolysis of acetyl-coenzyme A, a central metabolic intermediate, signals the brain and helps buffer stress. Using a chronic social defeat stress paradigm in male mice, we observed a hepatic glucose-to-acetate metabolic switch, followed by a glucocorticoid-repressed transcription of the acetyl-coenzyme A hydrolase, acetyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 12, to confer stress vulnerability. Hepatic overexpression of acetyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 12 alleviated depression-like phenotypes via increasing acetate output to promote histone acetylation in the ventral hippocampus, which bolstered the expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 in astrocytes, limiting neuroinflammation and rescuing inhibitory synaptic transmission dysfunction. Our findings demonstrate that hepatic acetyl-coenzyme A hydrolysis serves as a key liver-brain axis component that regulates depression susceptibility.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.08.010
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00383-3
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
