近日,美国纽约城市大学Alu, Andrea团队研究了光子时间界面的电动力学。相关论文发表在2025年9月23日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
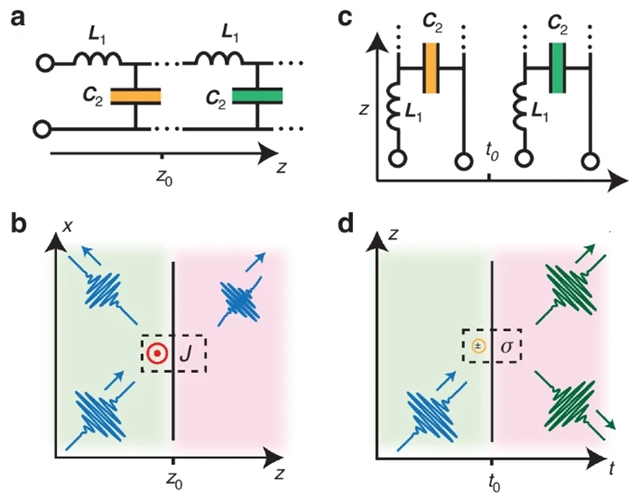
人们通过在空间和时间上对物质进行工程处理,已经出现了奇异的波浪控制形式。在这个框架下,在光子时间晶体和时空超材料的基础上,时间光子界面,即材料电磁特性的突变,已被证明可以诱导双重空间反射和折射的时间散射现象。尽管人们对这些应用进行了数十年的理论研究,以及最近的实验证明,但对这些现象的严谨建模一直落后。
研究组从第一性原理出发建立了时间光子界面电动力学的严谨模型,强调了驱动时间变化机制的关键作用。研究组证明了基于其微观实现,与时间散射相关的边界条件和守恒定律可能在很大程度上偏离文献中常用的那些。该结果为时变结构中光-物质相互作用的基础研究以及它们在光学和光子学中的未来实现和应用前景开辟了新的前景。
附:英文原文
Title: Electrodynamics of photonic temporal interfaces
Author: Galiffi, Emanuele, Sols, Diego Martnez, Yin, Shixiong, Engheta, Nader, Al, Andrea
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-23
Abstract: Exotic forms of wave control have been emerging by engineering matter in space and time. In this framework, temporal photonic interfaces, i.e., abrupt changes in the electromagnetic properties of a material, have been shown to induce temporal scattering phenomena dual to spatial reflection and refraction, at the basis of photonic time crystals and space-time metamaterials. Despite decades-old theoretical studies on these topics, and recent experimental demonstrations, the careful modeling of these phenomena has been lagging behind. Here, we develop from first principles a rigorous model of the electrodynamics of temporal photonic interfaces, highlighting the crucial role of the mechanisms driving time variations. We demonstrate that the boundary conditions and conservation laws associated with temporal scattering may substantially deviate from those commonly employed in the literature, based on their microscopic implementation. Our results open new vistas for both fundamental investigations over light–matter interactions in time-varying structures and for the prospect of their future implementations and applications in optics and photonics.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01947-2
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01947-2
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
