近日,北京大学樊新元团队报道了光催化标记支持亚细胞分辨RNA分析和同步多组学研究。相关论文发表在2025年9月16日出版的《自然-化学》杂志上。
理解健康和疾病中的细胞功能需要解剖亚细胞转录组的时空变化。现有的线粒体RNA谱分析方法存在局限性,包括低分辨率、污染和依赖基因操作。
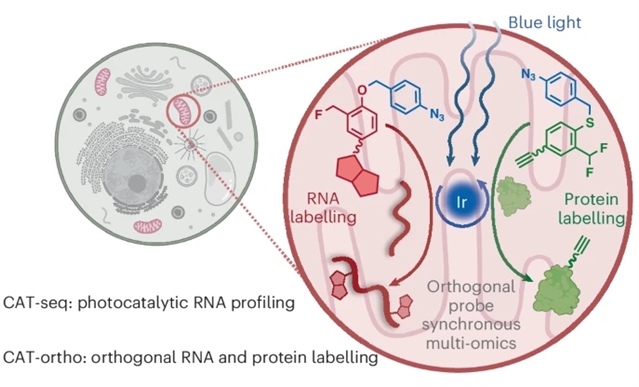
研究组提出了一种生物正交光催化标记和测序策略(CAT-seq),可以在没有遗传操作的情况下对活细胞中的线粒体RNA进行高分辨率的原位分析。他们鉴定了一种醌类探针,用于高效的RNA标记。严格的验证和优化使CAT-seq能够成功地分析线粒体RNA并跟踪HeLa细胞中的RNA动力学。
研究组进一步将CAT-seq应用于具有挑战性的RAW 264.7巨噬细胞,揭示了潜在的线粒体翻译重塑途径。通过利用醌甲基弹头的化学性质,研究组建立了一个正交标记系统,可以在同一样品中同步进行RNA和蛋白质多组学分析。在生物正交光催化化学的辅助下,CAT-seq为亚细胞分辨RNA和多组学研究提供了一种通用的、非遗传的、良好兼容的方法,特别是在完整的初级活样本研究中,否则很难获得。
附:英文原文
Title: Photocatalytic labelling-enabled subcellular-resolved RNA profiling and synchronous multi-omics investigation
Author: Bi, Yunpeng, Yu, Lishan, Deng, Qidong, Kong, Linghao, Guo, Fuhu, Zhang, Yuchen, Wang, Ruixiang, Chen, Peng R., Liu, Jun, Fan, Xinyuan
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-16
Abstract: Understanding cellular functions in health and disease requires dissecting spatiotemporal variations in the subcellular transcriptome. Existing methods for mitochondrial RNA profiling suffer from limitations, including low resolution, contamination and dependence on genetic manipulation. Here we present a bioorthogonal photocatalytic labelling and sequencing strategy (CAT-seq) that enables high-resolution, in situ profiling of mitochondrial RNA in living cells without genetic manipulation. We identified a quinone methide probe for efficient RNA labelling. Rigorous validation and optimization enabled CAT-seq to successfully profile mitochondrial RNA and track RNA dynamics in HeLa cells. We further applied CAT-seq to the challenging RAW 264.7 macrophages, revealing an underlying mitochondrial translational remodelling pathway. By leveraging the chemistry of quinone methide warheads, we established an orthogonal labelling system enabling synchronous RNA and protein multi-omics profiling within the same sample. Together, assisted by bioorthogonal photocatalytic chemistry, CAT-seq offers a general, non-genetic and well-compatible approach for subcellular-resolved RNA and multi-omics investigations, particularly in studies of intact primary living samples that are otherwise challenging to access.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01946-1
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01946-1
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
