近日,西湖大学张彪彪团队实现了长寿命NiOOH相中的保留电荷驱动催化水氧化。该研究于2025年9月15日发表在《自然-化学》杂志上。
NiOOH作为水氧化催化剂已被广泛研究,但其在操作条件下的活性结构和催化机理尚不清楚。分离真活性相对进一步深入探索析氧反应机理具有重要意义。
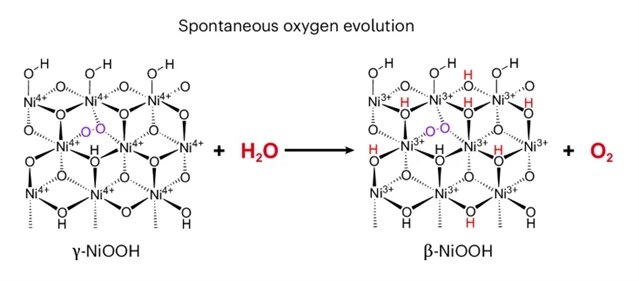
研究组成功分离出具有丰富Ni4+的长寿命活性NiOOH相,并在电化学析氧反应过程中检测到稳定的Ni-O-O-Ni2相的存在。这一相在室温下在纯水中自发地、连续地释放氧气,持续数分钟,而不需要外加电位。通过在线质谱分析,研究组证明了自发的析氧过程是通过初始的晶格氧偶联进行的,随后在活性位点进行了连续的水氧化。通过对这一过程的研究,研究组发现NiOOH体中储存的Ni4+电荷可以不断地迁移到表面活性位点,从而驱动水氧化。这为设计更先进的水氧化催化剂提供了指导,并在分子水平上提供了见解。
附:英文原文
Title: Reserved charges in a long-lived NiOOH phase drive catalytic water oxidation
Author: Cui, Xin, Ding, Yunxuan, Zhang, Feiyang, Cao, Xing, Guo, Yu, Sun, Licheng, Zhang, Biaobiao
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-15
Abstract: Although NiOOH has been widely studied as a water oxidation catalyst, its active structure and catalytic mechanism under operating conditions remain unclear. Isolating the true active phase is of great significance for further exploring the oxygen evolution reaction mechanisms in depth. Here we successfully isolated a long-lived active NiOOH phase with abundant Ni4+ and detected the presence of a stable Ni–O–O–Ni2 phase in the bulk during the electrochemical oxygen evolution reaction. This phase spontaneously and continuously evolves oxygen in pure water at room temperature for several minutes without requiring an applied potential. Through online mass spectrometry, we demonstrate that spontaneous oxygen evolution proceeds via initial lattice oxygen coupling followed by continuous water oxidation at active sites. By studying this process, we show that the charges stored by the Ni4+ in NiOOH bulk can continuously migrate to the surface active sites to drive water oxidation. This offers guidance for the design of more advanced water oxidation catalysts and provides insights at the molecular level.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01942-5
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01942-5
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
