美国密歇根大学Jonathan Terhorst课题组研制了基于重组序列数据的种群规模历史加速贝叶斯推断。2025年9月15日出版的《自然—遗传学》发表了这项成果。
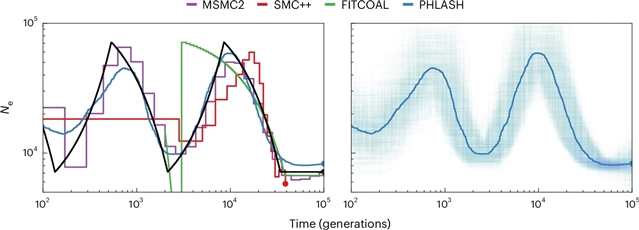
了一种从全基因组序列数据推断种群历史的新方法——平均采样历史学习法(PHLASH)。它的工作原理是,从成对顺序马尔可夫聚结样模型的后验分布中绘制聚结强度函数的随机低维投影,并将它们平均起来,形成一个准确的自适应估计器。在模拟数据上,PHLASH比几种竞争方法(包括SMC++、MSMC2和FITCOAL)速度更快,误差更小。
此外,它提供了自动不确定性量化,并导致新的贝叶斯测试程序来检测人口结构和古老的瓶颈。关键的技术进步是一种计算聚结隐马尔可夫模型的分数函数(对数似然梯度)的新算法,该算法的计算成本与计算对数似然相同。PHLASH已经作为一个易于主题化的Python软件包发布,并在可用时利用图形处理单元加速。
附:英文原文
Title: Accelerated Bayesian inference of population size history from recombining sequence data
Author: Terhorst, Jonathan
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-15
Abstract: This study introduces population history learning by averaging sampled histories (PHLASH), a new method for inferring population history from whole-genome sequence data. It works by drawing random, low-dimensional projections of the coalescent intensity function from the posterior distribution of a pairwise sequentially Markovian coalescent-like model and averaging them together to form an accurate and adaptive estimator. On simulated data, PHLASH tends to be faster and have lower error than several competing methods, including SMC++, MSMC2 and FITCOAL. Moreover, it provides automatic uncertainty quantification and leads to new Bayesian testing procedures for detecting population structure and ancient bottlenecks. The key technical advance is a new algorithm for computing the score function (gradient of the log likelihood) of a coalescent hidden Markov model, which has the same computational cost as evaluating the log likelihood. PHLASH has been released as an easy-to-use Python software package and leverages graphics processing unit acceleration when available.
DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02323-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02323-x
Nature Genetics:《自然—遗传学》,创刊于1992年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:41.307
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/ng/
投稿链接:https://mts-ng.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
