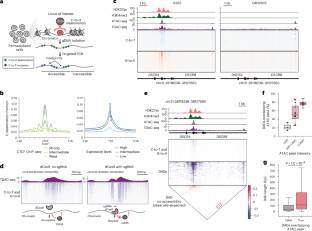
近日,美国麻省理工学院和哈佛大学的布罗德研究所教授Brian B. Liau及其研究团队报道了使用双链DNA脱氨酶耦合CRISPR扫描与靶向染色质可及性分析。相关论文于2025年9月11日发表在《自然—方法学》杂志上。
在这里,课题组人员利用双链DNA胞苷脱氨酶,通过靶向PCR和长读测序(一种课题组人员称为靶向脱氨酶可及染色质测序(TDAC-seq)的方法,来分析内源性酶感兴趣位点的染色质可及性。TDAC-seq在目标位点上具有高序列覆盖率,可以与CRISPR扰动结合,以单核苷酸分辨率将基因编辑及其对同一单个染色质纤维上染色质可及性的影响联系起来。该研究团队使用TDAC-seq分析了在红系分化过程中激活人CD34+造血干细胞和祖细胞(HSPCs)中胎儿血红蛋白的CRISPR编辑,以及在汇集的CRISPR和碱基编辑屏幕中覆盖控制珠蛋白位点的增强子。课题组人员进一步扩展了该方法,在CD34+ HSPCs的单个合并CRISPR实验中询问与骨髓增生性肿瘤风险相关的GFI1B连接增强子中的947个变体。总之,TDAC-seq通过基因组编辑实现了单分子染色质纤维的高分辨率序列功能定位。
据悉,基因组编辑使内源性顺式调控元件的序列功能分析成为可能,从而推动对其机制的理解。然而,这些方法缺乏直接的、可扩展的跨长单分子染色质纤维的染色质可及性读数。
附:英文原文
Title: Coupling CRISPR scanning with targeted chromatin accessibility profiling using a double-stranded DNA deaminase
Author: Roh, Heejin, Shen, Simon P., Hu, Yan, Kwok, Hui Si, Siegenfeld, Allison P., Lee, Ceejay, Zepeda, Marcanthony U., Guo, Chun-Jie, Roseman, Shelby A., Comenho, Caroline, Sankaran, Vijay G., Buenrostro, Jason D., Liau, Brian B.
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-11
Abstract: Genome editing enables sequence-function profiling of endogenous cis-regulatory elements, driving understanding of their mechanisms. However, these approaches lack direct, scalable readouts of chromatin accessibility across long single-molecule chromatin fibers. Here we leverage double-stranded DNA cytidine deaminases to profile chromatin accessibility at endogenous loci of interest through targeted PCR and long-read sequencing, a method we term targeted deaminase-accessible chromatin sequencing (TDAC-seq). With high sequence coverage at targeted loci, TDAC-seq can be integrated with CRISPR perturbations to link genetic edits and their effects on chromatin accessibility on the same single chromatin fiber at single-nucleotide resolution. We employed TDAC-seq to parse CRISPR edits that activate fetal hemoglobin in human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) during erythroid differentiation as well as in pooled CRISPR and base-editing screens tiling an enhancer controlling the globin locus. We further scaled the method to interrogate 947 variants in a GFI1B-linked enhancer associated with myeloproliferative neoplasm risk in a single pooled CRISPR experiment in CD34+ HSPCs. Together, TDAC-seq enables high-resolution sequence-function mapping of single-molecule chromatin fibers by genome editing.
DOI: 10.1038/s41592-025-02811-2
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02811-2
Nature Methods:《自然—方法学》,创刊于2004年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:47.99
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nmeth/
投稿链接:https://mts-nmeth.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
