浙江大学刘志红课题组揭示了PLD4的功能缺失突变可导致系统性红斑狼疮。2025年9月10日出版的《自然》发表了这项成果。
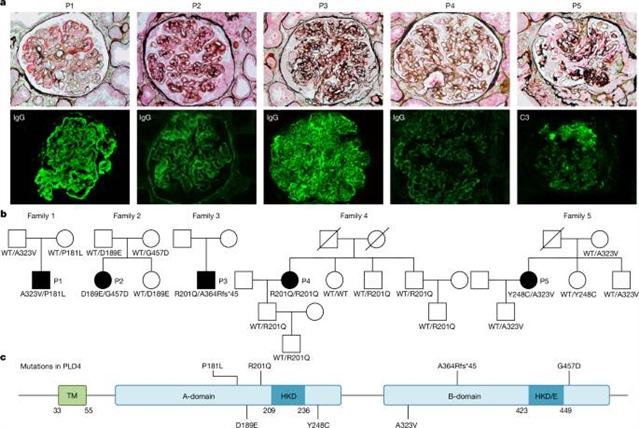
在这里,课题组研究人员报告了5例携带磷脂酶D家族成员4 (PLD4)隐性突变的SLE患者。在体外和离体实验中,PLD4的Deleteriothem变异导致单链核酸外切酶活性受损。PLD4功能缺失突变导致toll样受体7 (TLR7)和TLR9过度激活。下游炎症信号通路,尤其是I型干扰素信号通路,在患者树突状细胞中被过度激活。PLD4缺陷小鼠表现出自身免疫和浆细胞样树突状细胞和浆细胞的细胞内扩增。PLD4缺陷小鼠对JAK抑制剂baricitinib有应答,提示靶向I型干扰素可能是PLD4缺陷患者的一种潜在治疗方法。
据了解,单基因红斑狼疮为系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)的潜在机制和治疗方法提供了有价值的见解。
附:英文原文
Title: Loss-of-function mutations in PLD4 lead to systemic lupus erythematosus
Author: Wang, Qintao, Zhu, Honghao, Sun, Xiangwei, Zhang, Changming, Ma, Shuangyue, Jin, Ying, Fu, Jinjian, Liu, Chenlu, Peng, Jiahui, Wang, Ruoran, Liu, Lin, Zeng, Yi, Gong, Cheng, Zhou, Qing, Yu, Xiaomin, Liu, Zhihong
Issue&Volume: 2025-09-10
Abstract: Monogenic lupus offers valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms and therapeutic approaches for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)1,2,3. Here we report on five patients with SLE carrying recessive mutations in phospholipase D family member 4 (PLD4). Deleterious variants in PLD4 resulted in impaired single-stranded nucleic acid exonuclease activity in in vitro and ex vivo assays. PLD4 loss-of-function mutations led to excessive activation of Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) and TLR9. Downstream inflammatory signalling pathways, especially type I interferon signalling, were hyperactivated in patient dendritic cells. Pld4-deficient mice presented with autoimmunity and cell-intrinsic expansion of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and plasma cells. Pld4-deficient mice responded to the JAK inhibitor baricitinib, suggesting that targeting type I interferon may be a potential therapy for patients with PLD4 deficiency.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09513-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09513-x
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
