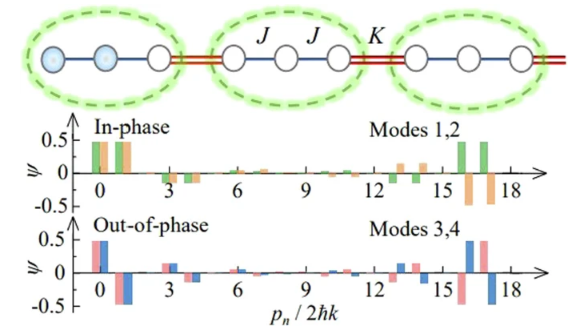
近日,山西大学马杰团队研究了相互作用原子三聚体阵列中非线性边缘态的观测。相关论文于2025年8月28日发表在《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
探索拓扑和非线性之间的相互作用导致了非线性拓扑物理学的一个新兴领域,它将拓扑状态的迷人特性的研究扩展到粒子之间的相互作用不能被忽视的状态。对于超冷原子系统,虽然最近已经观察到许多奇异的拓扑状态,但非线性效应仍然存在。
基于激光驱动的离散原子动量态耦合,研究组合成了一个拓扑三聚体阵列,其中原子相互作用产生可调谐的非线性。他们观察到密度种群进化和参与比随着相互作用的增加而形成非线性边缘态,而非拓扑阵列在大相互作用范围内差分输运。此外,研究组还展示了相互作用对种群分布的影响,从初始的单点种群进化而来。该工作为探索超冷原子气体中涌现的非线性拓扑行为开辟了道路。
附:英文原文
Title: Observation of nonlinear edge states in an interacting atomic trimer array
Author: Du, Huiying, Zhao, Hongxing, Li, Yuqing, Wang, Yunfei, Li, Rujiang, Wu, Jizhou, Liu, Wenliang, Zhang, Yiqi, Xiao, Liantuan, Jia, Suotang, Ma, Jie
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-28
Abstract: Exploring the interplay between topology and nonlinearity leads to an emerging field of nonlinear topological physics, which extends the study of fascinating properties of topological states to a regime where interactions between the particles cannot be neglected. For ultracold atomic systems, although many exotic topological states have been recently observed, the nonlinear effect remains elusive. Here, based on the laser-driven couplings of discrete atomic momentum states, we synthesize a topological trimer array, where the atomic interactions give rise to tunable nonlinearities. We observe the formation of nonlinear edge states in the density population evolution and participation ratio with increasing interaction, in contrast to the diffusive transport in a broad interaction range in nontopological arrays. Furthermore, we show the impact of interactions on the population distribution evolved from the initialized single-site population. Our work opens the avenue for exploring emergent nonlinear topological behaviors in ultracold atomic gases.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01997-6
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01997-6
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
