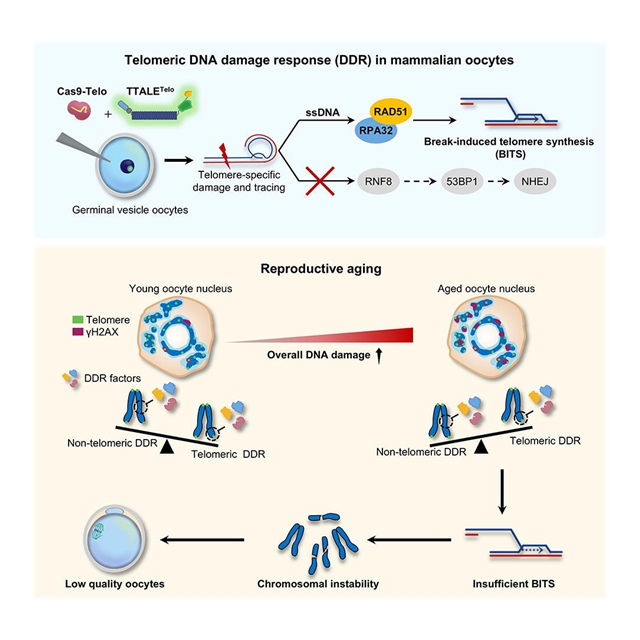
课题组人员观察到衰老的人生发囊(GV)卵母细胞累积了端粒DNA损伤。接下来,该团队利用CRISPR/Cas9在单核母细胞中建立了端粒DNA损伤模型,该模型表现出染色体不稳定性增加和减数分裂成熟受损。
此外,卵母细胞的端粒DNA损伤不会启动端粒融合,而是加速端粒运动并触发断裂诱导的端粒合成(BITS)。机制上,RPA32和RAD51被招募到受损的端粒,并与ATR和PARP1一起促进BITS。
然而,端粒DNA损伤在完全成熟的卵母细胞中募集很少的RNF8,可能阻碍了53BP1的募集。尽管随着母亲年龄的增长,GV卵母细胞中RAD51促进的DNA修复的总体活性变化很小,但这种DDR机制优先参与衰老卵母细胞的非端粒区域。因此,当遇到端粒DNA损伤时,衰老的卵母细胞可能会出现端粒DDR和BITS不足。总之,他们的研究阐明了端粒DDR招募关键因子(如RAD51)来激活BITS,并且端粒DDR不足会增加衰老卵母细胞中染色体的不稳定性。
据了解,染色体不稳定性的增加会损害卵母细胞的质量,导致女性生殖老化。端粒DNA损伤反应(DDR)对基因组稳定性至关重要,然而,卵母细胞如何对端粒损伤作出反应仍然是未知的。
附:英文原文
Title: Insufficient telomeric DNA damage response promotes chromosomal instability in aged oocytes
Author: Fenghua Liu c, Junjiu Huang a b
Issue&Volume: 2025/08/25
Abstract: Increased chromosomal instability impairs oocyte quality, contributing to female reproductive aging. The telomeric DNA damage response (DDR) is essential for genomic stability, however, how oocytes respond to telomeric damage remains elusive. Here, we observed that aged human germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes accumulated telomeric DNA damage. We next established a telomeric DNA damage model with CRISPR/Cas9 in mouse oocytes, which exhibited increased chromosome instability and impaired meiotic maturation. Furthermore, telomeric DNA damage in oocytes did not initiate telomere fusion but rather accelerated telomere movement and triggered break-induced telomere synthesis (BITS). Mechanistically, RPA32 and RAD51 were recruited to damaged telomeres, and contributed to BITS along with ATR and PARP1. However, telomeric DNA damage recruited few RNF8 in fully grown oocytes, possibly impeding the 53BP1 recruitment. Despite minimal changes in the overall activity of RAD51-promoted DNA repair in GV oocytes with maternal age, this DDR machinery was preferentially involved in non-telomeric regions in aged oocytes. Consequently, upon encountering telomeric DNA damage, aged oocytes might undergo insufficient telomeric DDR and BITS. Together, our study illustrates that telomeric DDR recruits key factors, such as RAD51, to activate BITS, and that insufficient telomeric DDR increases chromosomal instability in aged oocytes.
DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2025.08.034
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2095927325008655
Science Bulletin:《科学通报》,创刊于1950年。隶属于SciEngine出版平台,最新IF:18.9
官方网址:https://www.sciengine.com/SB/home
投稿链接:https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/csb
