近日,德国柏林洪堡大学Fiedler, Dorothea团队揭示了核苷二磷酸激酶A (NME1)催化其自身的寡磷酸化。相关论文发表在2025年8月20日出版的《自然-化学》杂志上。
蛋白磷酸化是真核细胞的一个重要信号传导机制。这种翻译后修饰的范围包括蛋白质热磷酸化和多磷酸化。
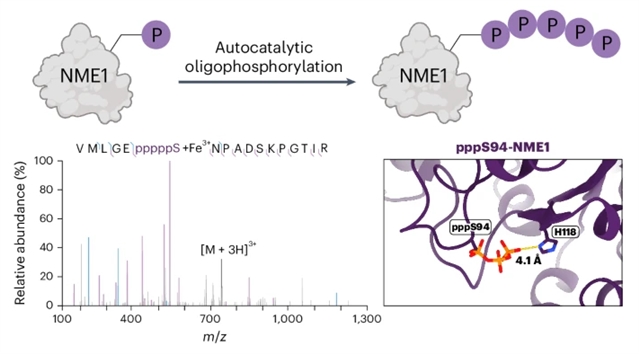
研究组报道了另一种磷酸化模式的发现:蛋白质寡磷酸化。利用位点特异性磷酸化和焦磷酸化核苷二磷酸激酶A (NME1),研究了这些修饰对酶活性的影响。Thr94上的磷酸化,尤其是焦磷酸化,降低了核苷二磷酸激酶的活性。然而,磷蛋白和焦磷蛋白都催化它们自己的寡磷酸化——形成六磷酸链主题化ATP作为辅助因子。
寡磷酸化严重依赖于催化组氨酸残基His118,对修饰蛋白的低温电镜分析表明,这是一种分子内磷酸化转移机制。在生化样品和细胞裂解物中,NME1的寡磷酸化进一步被主题质谱法证实,并被发现促进了一组新的蛋白质相互作用。该结果强调了磷酸化调控的复杂性,这里描述的方法为将来研究这种非自然修饰的影响提供了机会。
附:英文原文
Title: Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A (NME1) catalyses its own oligophosphorylation
Author: Celik, Arif, Schpf, Felix, Stieger, Christian E., Lampe, Sarah, Hanf, Bjrn, Morgan, Jeremy A. M., Ruwolt, Max, Liu, Fan, Hackenberger, Christian P. R., Roderer, Daniel, Fiedler, Dorothea
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-20
Abstract: Protein phosphorylation is a central signalling mechanism in eukaryotic cells. The scope of this post-translational modification includes protein pyro- and polyphosphorylation. Here we report the discovery of another mode of phosphorylation: protein oligophosphorylation. Using site-specifically phosphorylated and pyrophosphorylated nucleoside diphosphate kinase A (NME1), the effects of these modifications on enzyme activity were investigated. Phosphorylation, and more so pyrophosphorylation, on Thr94 reduced the nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity. Nevertheless, both phosphoprotein and pyrophosphoprotein catalysed their own oligophosphorylation—up to the formation of a hexaphosphate chain—using ATP as a cofactor. Oligophosphorylation was critically dependent on the catalytic histidine residue His118, and cryogenic electron microscopy analysis of the modified proteins suggests an intramolecular phosphoryl transfer mechanism. Oligophosphorylation of NME1 in biochemical samples, and in cell lysates, was further confirmed using mass spectrometry, and was found to promote a new set of protein interactions. Our results highlight the complex nature of phosphoregulation, and the methods described here provide the opportunity to investigate the impact of this unusual modification in the future.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01915-8
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01915-8
Nature Chemistry:《自然—化学》,创刊于2009年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:24.274
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nchem/
投稿链接:https://mts-nchem.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
