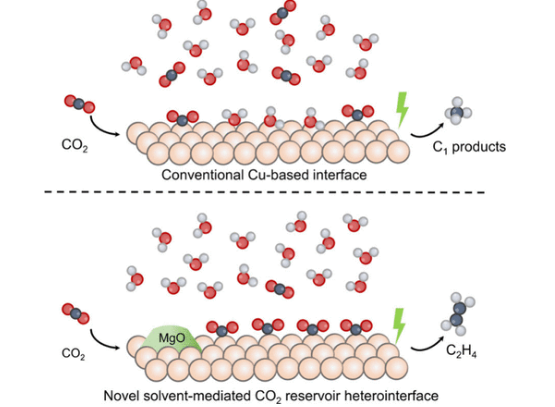
将废弃的二氧化碳转化为增值燃料和化学品,同时实现可再生电力储存,是实现可持续能源经济的可行战略。然而,高效转化为C2+产品仍然具有挑战性,主要是由于在水环境中催化剂表面的CO2浓度较低。
研究组通过设计具有丰富纳米界面的Cu2O-MgO催化剂来解决这一问题,这些催化剂在水条件下可作为有效的CO2储层。从头算分子动力学模拟表明,这些界面极大地增强了CO2在表面的稳定性,有效地抑制了它们被界面水分子取代。这种局部CO2富集促进了C-C耦合动力学,选择性地促进了目标产物的形成。在此基础上,研究组合成了具有丰富Cu2O-MgO纳米界面的模型催化剂,并评估了其在水介质中的性能。
值得一提的是,流动电解槽试验表明,在电流密度为~ 240 mA·cm-2时,乙烯的法拉第效率为67%。随后的机理研究结合光谱实验和理论计算模拟表明,表面富集的CO2增强了Cu活性位点的CO*覆盖,从而通过促进C-C偶联促进乙烯的生成。该研究开创了多相催化剂的合理设计,可用于选择性CO2RR处理增值化学品,并具有扩展到各种电催化过程的潜在应用。
附:英文原文
Title: Tailoring Solvent-Mediated CO2 Reservoirs at Heterointerfaces for Enhanced Electrochemical CO2-to-C2H4 Conversion
Author: Jing Yang, Chengkai Jin, Di Si, Fusong Kang, Fen Qiao, Junfeng Wang, Dongjing Liu, Lilin Zhang, Tian Tian, Xunhua Zhao, Zhou Yu, Kang Chen, Heng-Quan Chen, Xiao-Shun Zhou
Issue&Volume: August 12, 2025
Abstract: Transforming waste CO2 into value-added fuels and chemicals, while simultaneously enabling renewable electricity storage, presents a viable strategy for achieving a sustainable energy economy. However, efficient conversion to C2+ products remains challenging, primarily due to the low CO2 concentration at the catalyst surface in aqueous environments. Herein, we addressed this issue by designing Cu2O-MgO catalysts with abundant nanointerfaces serving as effective CO2 reservoirs under aqueous conditions. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations demonstrated that these interfaces substantially enhanced the CO2 stabilization at the surface, effectively inhibiting their displacement by interfacial water molecules. This localized CO2 enrichment facilitated C–C coupling kinetics and selectively promoted the formation of target products. Building on these findings, we synthesized a model catalyst featuring abundant Cu2O-MgO nanointerfaces and evaluated its performance in aqueous media. Remarkably, flowing electrolyzer tests demonstrated a Faradaic efficiency of 67% for ethylene at a current density of ~ 240 mA·cm–2. Subsequent mechanistic investigations combining spectroscopy experiments and theoretical calculation simulations demonstrated that the surface-enriched CO2 enhanced the CO* coverage at the Cu active sites, thereby promoting ethylene production through facilitated C–C coupling. This study pioneers the rational design of heterogeneous catalysts for selective CO2RR toward value-added chemicals with potential applications extending to diverse electrocatalytic processes.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c06799
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c06799
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
