瑞士苏黎世大学Soeren S. Lienkamp小组宣布他们开发出基于微同源模板的深度学习辅助设计精确、可预测的基因组整合。2025年8月12日,国际知名学术期刊《自然—生物技术》发表了这一成果。
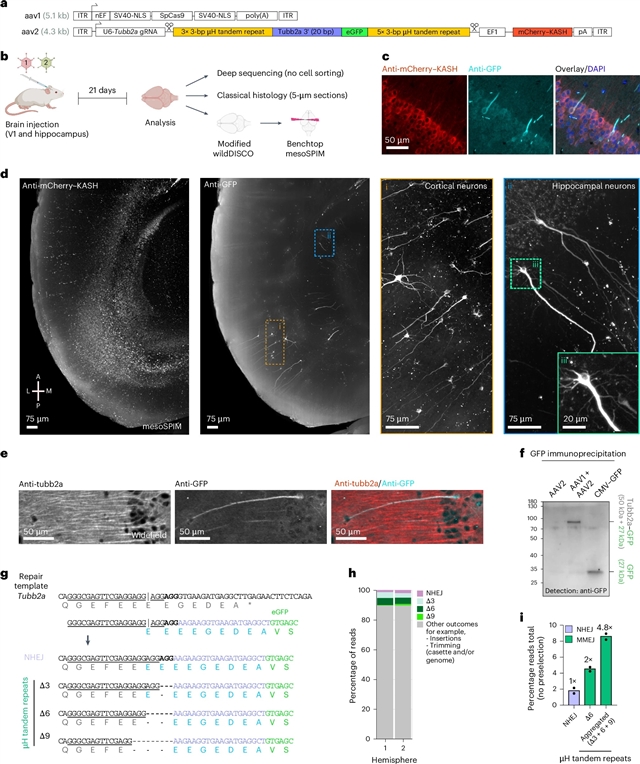
研究小组发现基因组-货物界面的修复是可以通过深度学习模型预测的,并且遵循特定于序列上下文的规则。在计算机预测的基础上,课题组人员设计了一种碱基对串联重复修复臂匹配双链断裂微同源的策略。这些重复同源臂促进框架保留盒整合,减少靶位点和转基因内的缺失。该课题组证实了HEK293T细胞中32个位点的精确整合。种系可传递的转基因整合和内源性蛋白标记在非洲爪蟾和成年无主脑中证实了在早期胚胎分裂和未分裂分化细胞中的精确整合。优化的修复臂也促进了体外和体内对无疤痕的单核苷酸或双核苷酸改变主题寡核苷酸模板的小编辑。该课题组提供设计工具Pythia,以促进精确的基因组整合和编辑,用于广泛的靶细胞类型和应用的实验和治疗目的。
研究人员表示,精确的基于CRISPR的DNA整合和编辑仍然具有挑战性,主要是因为对修复过程的控制不足。
附:英文原文
Title: Precise, predictable genome integrations by deep-learning-assisted design of microhomology-based templates
Author: Naert, Thomas, Yamamoto, Taiyo, Han, Shuting, Rck, Ruth, Horn, Melanie, Bethge, Philipp, Vladimirov, Nikita, Voigt, Fabian F., Figueiro-Silva, Joana, Bachmann-Gagescu, Ruxandra, Vleminckx, Kris, Helmchen, Fritjof, Lienkamp, Soeren S.
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-12
Abstract: Precise CRISPR-based DNA integration and editing remain challenging, largely because of insufficient control of the repair process. We find that repair at the genome–cargo interface is predictable by deep learning models and adheres to sequence-context-specific rules. On the basis of in silico predictions, we devised a strategy of base-pair tandem repeat repair arms matching microhomologies at double-strand breaks. These repeat homology arms promote frame-retentive cassette integration and reduce deletions both at the target site and within the transgene. We demonstrate precise integrations at 32 loci in HEK293T cells. Germline-transmissible transgene integration and endogenous protein tagging in Xenopus and adult mouse brains demonstrated precise integration during early embryonic cleavage and in nondividing, differentiated cells. Optimized repair arms also facilitated small edits for scarless single-nucleotide or double-nucleotide changes using oligonucleotide templates in vitro and in vivo. We provide the design tool Pythia to facilitate precise genomic integration and editing for experimental and therapeutic purposes for a wide range of target cell types and applications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41587-025-02771-0
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-025-02771-0
Nature Biotechnology:《自然—生物技术》,创刊于1996年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:68.164
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/nbt/
投稿链接:https://mts-nbt.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
