近日,苏州大学曹国洋团队研究了基于手性等离子体超材料的电增益辅助圆偏振光探测。这一研究成果发表在2025年8月11日出版的《光:科学与应用》杂志上。
基于手性有机材料或无机结构的圆偏振光(CPL)探测器具有高度集成片上应用的巨大潜力;然而,这些器件通常必须在不对称系数(g)、响应度(R)和稳定性之间寻求最佳平衡。
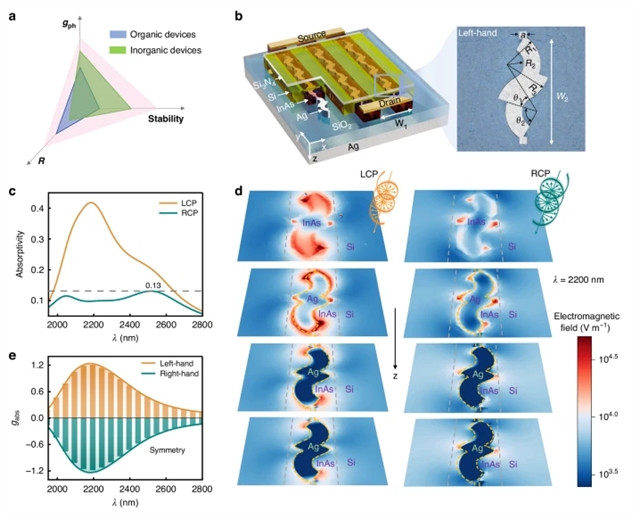
研究组的目标是通过将手性无机等离子体超材料与电增益相结合来打破这一限制,通过这种方法可以同时增强g和R,同时确保稳定性。他们展示了一种基于“S”形手性银纳米线/InAs/Si异质结构的CPL探测器,其中“S”形手性银纳米线与覆盖的InAs通道的精细结构使得InAs中的吸收不对称,这是由于左圆极化和右圆极化(LCP和RCP)光激发的不同局部表面等离子体共振。
砷化铟(InAs)作为导电通道,通过光门效应、栅极调制及陷阱效应的协同作用实现显著的光电导增益。所提出的无机稳定器件具备以下优异性能:~1.56的高电学增益、~33,900安培/瓦的超高响应度、~1.8×1011 Jones的大比探测率,以及~23纳秒的超快响应时间,且在2微米至2.8微米的宽光谱范围内保持高性能。最终,通过将ASCII码的"1"和"0"分别编码于左旋圆偏振光(LCP)与右旋圆偏振光(RCP),并利用器件对这两种偏振光增强的甄别响应能力,我们在器件层面展示了一种简洁的无密钥光学加密通信方案,彰显其在系统级应用的广阔潜力。
附:英文原文
Title: Electrical-gain-assisted circularly polarized photodetection based on chiral plasmonic metamaterials
Author: Chen, Chenghao, Yang, Zhenhai, Hang, Tianyi, Hao, Yining, Chen, Yijing, Zhang, Chengzhuang, Yang, Jiong, Liu, Xiaoyi, Li, Xiaofeng, Cao, Guoyang
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-11
Abstract: Circularly polarized light (CPL) detectors based on chiral organic materials or inorganic structures hold great potential for highly integrated on-chip applications; however, these devices usually have to seek an optimal balance among the asymmetry factor (g), responsivity (R), and stability. Here, we aim to break such a limitation by combining chiral inorganic plasmonic metamaterials with electrical gain, by which one can enhance both g and R while simultaneously securing the stability. We demonstrate a CPL detector based on “S”-shaped chiral Ag nanowires/InAs/Si heterostructures, where the meticulous construction of the “S”-shaped chiral Ag nanowires with the overlaying InAs channel enables a substantial absorption asymmetry in InAs due to differentiated localized surface plasmon resonances excited by left- and right-circularly polarized (LCP and RCP) light. The InAs serves as a conductive channel, achieving significant electrical gain through photoconductive effects assisted by photogating, gate modulation, and trap effects. The proposed inorganic stable device exhibits a high electrical g of ~1.56, an ultra-high R of ~33,900AW1, a large specific detectivity of ~1.8×1011 Jones, and an ultra-short response time of ~23ns, with the high performance achieved in a broad spectral range from 2μm to 2.8μm. Ultimately, by encoding ASCII code 1 and 0 onto LCP and RCP light, respectively, and leveraging the device’s heightened discrimination and response performance to these polarizations, we demonstrate a simple yet key-free optical encryption communication scheme at the device level, highlighting its extensive potential for system-level applications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41377-025-01932-9
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-025-01932-9
Light: Science & Applications:《光:科学与应用》,创刊于2012年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:19.4
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/lsa/
投稿链接:https://mts-lsa.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
