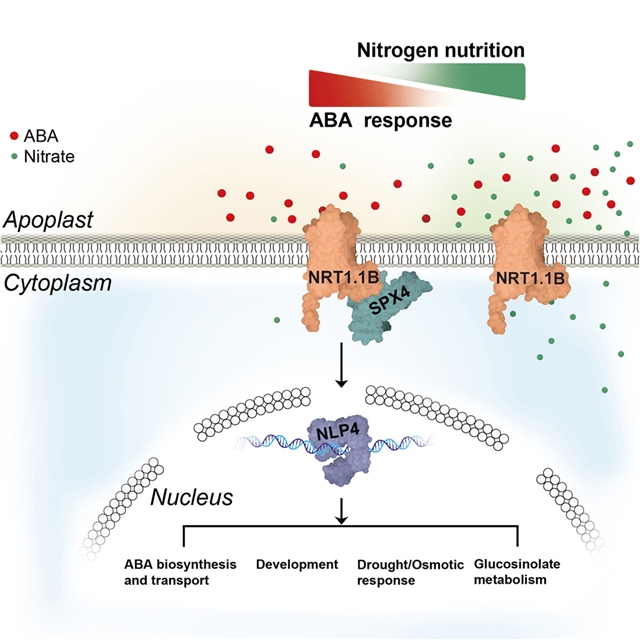
华南农业大学胡斌团队的研究显示,NRT1.1B作为脱落酸受体参与植物对复合环境信号的整合。2025年8月11日出版的《细胞》杂志发表了这项成果。
小组发现,在高硝酸盐条件下,ABA的转录反应被抑制,而在低硝酸盐条件下,ABA的转录反应显著增加,这表明ABA信号与营养条件紧密结合。有趣的是,NRT1.1B,传统上被认为是硝酸盐转运体和受体,对ABA表现出明显更高的亲和力,导致ABA促进NRT1.1B-SPX4复合物的形成。该复合体触发SPX4隔离的转录因子NLP4的释放,从而启动对ABA的转录反应。这些发现表明NRT1.1B具有ABA受体的功能。值得注意的是,硝酸盐和ABA与NRT1.1B的竞争性结合揭示了一种机制,使ABA能够对波动的营养条件做出灵活的反应,阐明了整合复合环境线索的复杂策略。
据悉,脱落酸(ABA)是植物适应环境条件最重要的激素。虽然植物中的ABA信号网络已经被广泛探索,但他们对各种ABA传感系统的理解仍然有限。
附:英文原文
Title: NRT1.1B acts as an abscisic acid receptor in integrating compound environmental cues for plants
Author: Xiaojun Ma, Wei Wang, Jingyi Zhang, Zhimin Jiang, Chengyuan Xu, Wenjun Zhu, Bihai Shi, Wanling Yang, Haiwei Su, Xiaohan Wang, Da Chen, Yanfei Wang, Juntao Wang, Jingchi Wang, Xiujie Liu, Xiaotian Wang, Xiahe Huang, Wenjun Xie, Yanting Cai, Ke Xu, Peiyong Xin, Linchuan Liu, Peitao Lü, Yingchun Wang, Jinfang Chu, Xin Gong, Chengcai Chu, Bin Hu
Issue&Volume: 2025-08-11
Abstract: Abscisic acid (ABA) is the most crucial phytohormone for plants in adapting to environmental conditions. While the ABA signaling network in plants has been extensively explored, our understanding of the diverse ABA sensing systems remains limited. Here, we found that the transcriptional response to ABA is suppressed under high-nitrate conditions but substantially increases under low-nitrate conditions, suggesting a tight integration of ABA signaling with nutrient conditions. Interestingly, NRT1.1B, traditionally recognized as a nitrate transporter and receptor, exhibits a markedly higher affinity for ABA, leading to the formation of an ABA-facilitated NRT1.1B-SPX4 complex. This complex triggers the release of SPX4-sequestered transcription factor NLP4, thereby initiating the transcriptional response to ABA. These findings establish that NRT1.1B functions as an ABA receptor. Notably, the competitive binding of nitrate and ABA to NRT1.1B unveils a mechanism that enables a flexible ABA response to fluctuating nutrient conditions, illustrating a sophisticated strategy for integrating compound environmental cues.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.07.027
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell/abstract/S0092-8674(25)00816-5
