近日,温州大学李林团队研究了离子-偶极相互作用调制阴离子增强的先进宽温钠离子电池的溶剂化化学。相关论文于2025年8月7日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
宽温钠离子电池(SIBs)被认为是极端温度条件下大规模储能系统的有希望的候选者。然而,SIB通常在高温下存在不稳定的电极-电解质界面(EEI),在低温下存在缓慢的界面动力学,导致其耐温性差,容量退化快。
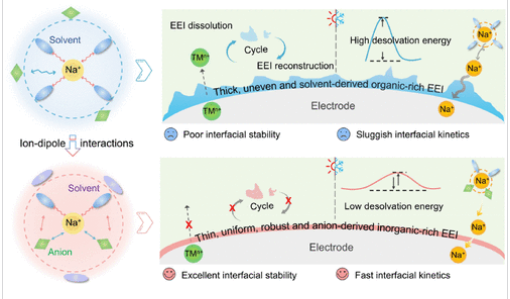
研究组采用弱配位羧酸酯助溶剂丁酸甲酯调节无氟酯基电解质中的离子偶极子相互作用,用于阴离子增强溶剂化化学。独特的溶剂化学特性使得在阴极和阳极表面构建稳定的阴离子衍生的富无机EEI,同时降低了脱溶能垒,从而显著提高了界面稳定性和动力学。因此,Prthemsian蓝||硬碳(PB||HC)全电池在- 20 ~ 100℃的宽温度范围内表现出稳定的工作性能。
值得注意的是,在55°C的高温下,经过230次循环后,PB||HC 18650圆柱形电池的容量保持率达到了91.41%。该研究为通过合理调节离子偶极子相互作用来设计无氟酯基电解质提供了有价值的指导,为宽温钠离子全电池铺平了一条有前景的道路。
附:英文原文
Title: Ion–Dipole Interactions Modulated Anion-Reinforced Solvation Chemistry for Advanced Wide-Temperature Sodium-Ion Full Batteries
Author: Yun Wan, Xiaoyan Shi, Zhiming Zhou, Wenxi Kuang, Xu Xu, Xiaosa Zhang, Xinhui Zeng, Xunzhu Zhou, Junxiang Liu, Shu-Lei Chou, Lin Li
Issue&Volume: August 7, 2025
Abstract: Wide-temperature sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are considered promising candidates for large-scale energy storage systems under extreme temperature conditions. However, SIBs generally suffer from an unstable electrode–electrolyte interface (EEI) at high temperature and sluggish interfacial kinetics at low temperature, resulting in poor temperature tolerance with fast capacity degradation. Herein, a weakly coordinated carboxylate ester cosolvent, methyl butyrate, is employed to modulate the ion–dipole interactions in fluorine-free ester-based electrolyte for the anion-reinforced solvation chemistry. The unique solvent chemistry enables the construction of stable anion-derived inorganic-rich EEI on both cathode and anode surfaces while simultaneously reducing the desolvation energy barrier, thereby significantly enhancing the interfacial stability and kinetics. Therefore, the Prussian blue||hard carbon (PB||HC) full cell demonstrates a stable operation at a wide temperature range from 20 to 100 °C. Noticeably, the PB||HC 18650 cylindrical cell delivers a superior capacity retention of 91.41% after 230 cycles at an elevated temperature of 55 °C. This work provides valuable guidance for designing fluorine-free ester-based electrolytes through rational modulation of ion–dipole interactions, paving a promising pathway for wide-temperature sodium-ion full batteries.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c07004
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c07004
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
