湖北大学曾明华团队近日揭示了原位配体转化促进分级Co19配位簇的串联组装-拆卸-重组。2025年7月4日出版的《结构化学》杂志发表了这项成果。
奇数和高核配位体极为罕见,但它们代表了一个有趣的子类,缺乏规则的重复构建块和高度的结构对称性,无法理解自组装的多原子系统。
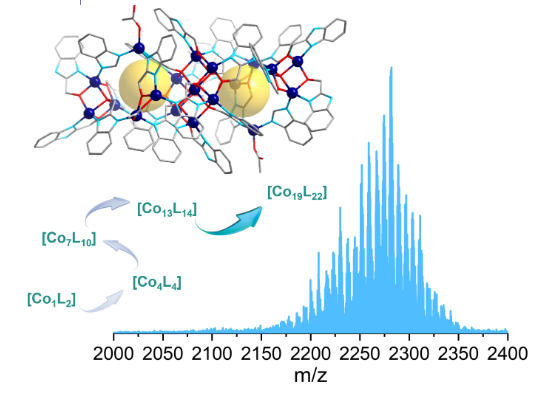
研究组通过原位配体从H2L1转化为L′,得到了最大的具有奇核特征的钴多齿配体基聚合物,即[Co19(HL1)8(L1)12(L′)2(Ac)4]·10CH3CH2OH·6H2O (1, H2L1= 1h -苯并[d]咪唑-2-基)甲醇,HL′= 1h -苯并[d]咪唑)。它具有分层三层和空笼式内部结构,由中央圆盘形[Co7L10]芯和两侧两个[Co6]环组成。晶体1的ESI-MS得到一系列超过16个片段,所有片段都具有一个集成的[Co19]核心,表明多核热计在溶液中的稳定性。
在从0到100 eV的持续能量增加期间,所有的MS峰都移到了较低的m/z范围内,但[Co19]核心保持完整,除了逐步消除多达3个Ac阴离子或3个L1连接体。反应沉积物的PXRD跟踪显示,在3 h时形成了[Co4L4]立方烷的关键前驱体,在6 h时含量下降,在12 h时消失,随后在18 h时生成清晰的溶液,出现晶体1,表明了初始的clthemter组装-拆卸过程。
反应沉积物和溶液的ESI-MS谱分析进一步确定了[Co7L10]圆盘及其膨胀[Co13L12(L’)2]的其他关键高核重组碎片的存在。提出了一种可能的串联组装-拆卸-重组机制:[CoL2]→[Co4L4]→[Co7L10]→[Co13L12(L′)2]→[Co19L20(L′)2]。它们的演化也表明,有机、无机和原位生成配体的协同作用,以及金属离子的不同配位几何形状,对奇数和高核配位聚合物的形成起着指向性作用。磁性分析表明,反铁磁耦合在磁体中起主导作用。
附:英文原文
Title: Tandem assembly-disassembly-reassembly of hierarchical Co19 coordination cluster facilitated by in-situ ligand transformation: Crystallography and ESI-MS revealed mechanism
Author: anonymous
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-04
Abstract: Odd-numbered and high-nuclearity coordination clusters are extremely rare, yet they represent an intriguing subclass lacking regular repeating building blocks and high structural symmetry for understanding self-assembled multiatomic systems. Herein, the largest cobalt and polydentate ligand based cluster featuring odd-nuclearity, namely [Co19(HL1)8(L1)12(L′)2(Ac)4]·10CH3CH2OH·6H2O (1, H2L1 = 1H-benzo[d]imidazole-2-yl)methanol, HL′ = 1H-benzo[d]imidazole), was obtained with in-situ ligand transformation from H2L1 to L′. It features a hierarchical trilayer and void-cage inside structure, consisting of central disc-shaped [Co7L10] core with two [Co6] rings on both sides. ESI-MS of crystal 1 yields a series of more than sixteen fragments, all featuring an integrated [Co19] core, suggesting stability of the polynuclear cluster in solution. During increased in-source energy from 0 to 100 eV, all MS peaks shifted to a lower m/z range, but the [Co19] core remained intact, excepting for the stepwise elimination of up to three Ac- anions or three L1 linkers. PXRD tracking of the reaction sediments showed the formation of a key precursor of [Co4L4] cubane at 3 h, and its content decreased at 6 h and vanished at 12 h, followed by the appearance of crystals 1 by generation of a clear solution at 18 h, suggesting an initial cluster assembly-disassembly process. ESI-MS spectra analysis of both reaction sediment and solution further identify the existence of other crucial higher-nuclearity reassembled fragments of [Co7L10] disk and its expansion of [Co13L12(L′)2]. A probable tandem assembly-disassembly-reassembly mechanism is put forward as [CoL2]→[Co4L4]→[Co7L10]→[Co13L12(L′)2]→[Co19L20(L′)2]. Their evolution also indicated the ingenious synergy of coexisting organic, inorganic and in-situ generated ligands, along with diverse coordination geometries of metal ions, plays a directional role in formation of odd-numbered and high-nuclearity coordination clusters. Magnetism analysis revealed antiferromagnetic coupling play dominated role in the cluster.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100659
Source: http://cjsc.ac.cn/cms/issues/827
Chinese Journal of Structural Chemistry:《结构化学》,创刊于1982年。隶属于中国结构化学杂志,最新IF:2.2
官方网址:http://cjsc.ac.cn/
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/cjschem/default2.aspx
