近日,
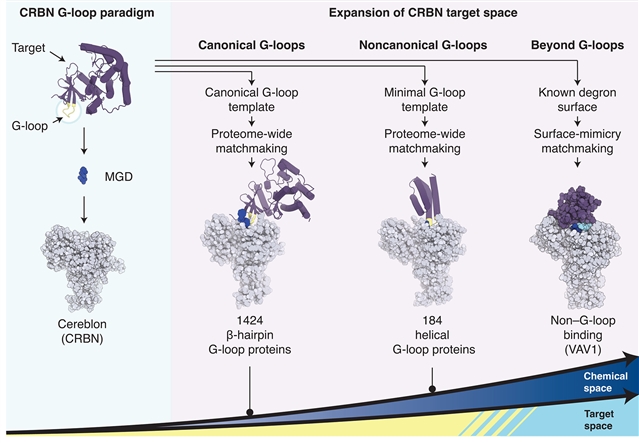
CRL4CRBN E3泛素连接酶是分子胶降解化合物的靶标,这些化合物重编程连接酶的特异性,诱导临床相关的新底物蛋白的降解。已知的小脑(CRBN)新底物共享一个可推广的β-发夹G环识别基序,允许系统地探索CRBN靶空间。基于计算挖掘方法的主题结构和基于表面的配对算法预测了人类蛋白质组中超过1600种CRBN兼容的G环蛋白,包括新发现的螺旋G环基序,并通过分子表面模仿机制确定了VAV1与CRBN结合的非规范新底物结合模式。这项工作拓宽了CRBN的靶标空间,重新定义了新底物识别的规则,并通过下一代分子胶降解剂重新利用CRL4CRBN,为消除具有挑战性的药物靶标建立了一个平台。
附:英文原文
Title: Mining the CRBN target space redefines rules for molecular glue–induced neosubstrate recognition
Author: Georg Petzold, Pablo Gainza, Stefano Annunziato, Ilaria Lamberto, Peter Trenh, Laura A. McAllister, Bradley DeMarco, Laura Schwander, Richard D. Bunker, Mary Zlotosch, Rohitha SriRamaratnam, Samuel Gilberto, Gerasimos Langousis, Etienne J. Donckele, Chao Quan, Vaik Strande, Gian Marco De Donatis, Shanique B. Alabi, Jessica Alers, Michelle Matysik, Camille Staehly, Aurélie Dubois, Arnaud Osmont, Mackenzie Garskovas, David Lyon, Lars Wiedmer, Vladimiras Oleinikovas, Raphael Lieberherr, Nooreen T. Rubin, Daniel T. Lam, Xavier Lucas, Elisa Liardo, Nina Ilic Widlund, Andreas Ritzén, Ramon Miguel Caceres, Dominico Vigil, Jennifer Tsai, Owen Wallace, Marisa Peluso, Amine Sadok, Ralph Tiedt, Alison M. Paterson, Vladislav Zarayskiy, Bernhard Fasching, Debora Bonenfant, Markus Warmuth, John C. Castle, Sharon A. Townson
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-03
Abstract: The CRL4CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase is the target of molecular glue degrader compounds that reprogram ligase specificity to induce the degradation of clinically relevant neosubstrate proteins. Known cereblon (CRBN) neosubstrates share a generalizable β-hairpin G-loop recognition motif that allows for the systematic exploration of the CRBN target space. Computational mining approaches using structure- and surface-based matchmaking algorithms predict more than 1600 CRBN-compatible G-loop proteins across the human proteome, including the newly discovered helical G-loop motif, and identify the noncanonical neosubstrate binding mode of VAV1 that engages CRBN through a molecular surface mimicry mechanism. This work broadens the CRBN target space, redefines rules for neosubstrate recognition, and establishes a platform for the elimination of challenging drug targets by repurposing CRL4CRBN through next-generation molecular glue degraders.
DOI: adt6736
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adt6736
