近日,美国遗传学系教授Megan Michel及其研究组报道了古代DNA揭示了乌拉尔人和叶尼塞人的史前生活。该研究于2025年7月2日发表于国际一流学术期刊《自然》杂志上。
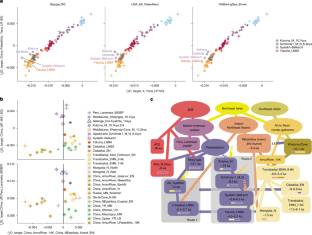
通过对该地区180个古代个体的全基因组数据进行分析,该研究组发现全新世早期到中期的狩猎采集者拥有一个连续的祖先梯度,从波罗的海地区的完全欧洲人到外贝加尔地区的完全东亚人。西伯利亚东北部的当代印第安人群体是偏离梯度的,他们是美洲原住民的主要祖先,然后与东亚内陆和阿穆尔河流域的人口混合,产生了两个人口,这两个人口的扩张与青铜时代前人口结构的崩溃相吻合。来自第一个种群的祖先,顺-贝加尔湖新石器-青铜时代晚期(Cisbaikal_LNBA),与说叶尼塞语的群体和与他们混合的群体有关,而来自第二个种群的祖先,雅库特新石器-青铜时代晚期(Yakutia_LNBA),与史前乌拉尔语的迁移有关。研究人员发现雅库特LNBA在大约4000年前首先从勒拿河流域向西分散到阿尔泰-萨扬地区,并进入与Seima-Turbino冶金有关的西西伯利亚社区,这是一套先进的青铜铸造技术,从阿尔泰开始爆炸式扩展。这16个Seima-Turbino时期的个体在他们的祖先上是多样化的,他们也有来自印度-伊朗相关的牧民和一系列狩猎采集者群体的DNA。因此,文化传播和移民都是Seima-Turbino现象的关键,这与早期乌拉尔语社区的最初传播有关。
研究人员表示,欧亚北部的森林和森林草原地区维持了数千年来北方人民之间的社会文化联系,但人们对它们的大部分历史知之甚少。特别是,今天讲乌拉尔语和叶尼塞语的人群的基因组形成是未知的。
附:英文原文
Title: Ancient DNA reveals the prehistory of the Uralic and Yeniseian peoples
Author: Zeng, Tian Chen, Vyazov, Leonid A., Kim, Alexander, Flegontov, Pavel, Sirak, Kendra, Maier, Robert, Lazaridis, Iosif, Akbari, Ali, Frachetti, Michael, Tishkin, Alexey A., Ryabogina, Natalia E., Agapov, Sergey A., Agapov, Danila S., Alekseev, Anatoliy N., Boeskorov, Gennady G., Derevianko, Anatoly P., Dyakonov, Viktor M., Enshin, Dmitry N., Fribus, Alexey V., Frolov, Yaroslav V., Grushin, Sergey P., Khokhlov, Alexander A., Kiryushin, Kirill Yu., Kiryushin, Yurii F., Kitov, Egor P., Kosintsev, Pavel, Kovtun, Igor V., Makarov, Nikolai P., Morozov, Viktor V., Nikolaev, Egor N., Rykun, Marina P., Savenkova, Tatyana M., Shchelchkova, Marina V., Shirokov, Vladimir, Skochina, Svetlana N., Sherstobitova, Olga S., Slepchenko, Sergey M., Solodovnikov, Konstantin N., Solovyova, Elena N., Stepanov, Aleksandr D., Timoshchenko, Aleksei A., Vdovin, Aleksandr S., Vybornov, Anton V., Balanovska, Elena V., Dryomov, Stanislav, Hellenthal, Garrett, Kidd, Kenneth, Krause, Johannes, Starikovskaya, Elena, Sukernik, Rem, Tatarinova, Tatiana, Thomas, Mark G., Zhabagin, Maxat, Callan, Kim, Cheronet, Olivia, Fernandes, Daniel, Keating, Denise, Candilio, Francesca, Iliev, Lora, Kearns, Aisling, zdoan, Kadir Toykan, Mah, Matthew, Micco, Adam, Michel, Megan
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-02
Abstract: The North Eurasian forest and forest-steppe zones have sustained millennia of sociocultural connections among northern peoples, but much of their history is poorly understood. In particular, the genomic formation of populations that speak Uralic and Yeniseian languages today is unknown. Here, by generating genome-wide data for 180 ancient individuals spanning this region, we show that the Early-to-Mid-Holocene hunter-gatherers harboured a continuous gradient of ancestry from fully European-related in the Baltic, to fully East Asian-related in the Transbaikal. Contemporaneous groups in Northeast Siberia were off-gradient and descended from a population that was the primary source for Native Americans, which then mixed with populations of Inland East Asia and the Amur River Basin to produce two populations whose expansion coincided with the collapse of pre-Bronze Age population structure. Ancestry from the first population, Cis-Baikal Late Neolithic–Bronze Age (Cisbaikal_LNBA), is associated with Yeniseian-speaking groups and those that admixed with them, and ancestry from the second, Yakutia Late Neolithic–Bronze Age (Yakutia_LNBA), is associated with migrations of prehistoric Uralic speakers. We show that Yakutia_LNBA first dispersed westwards from the Lena River Basin around 4,000 years ago into the Altai-Sayan region and into West Siberian communities associated with Seima-Turbino metallurgy—a suite of advanced bronze casting techniques that expanded explosively from the Altai1. The 16 Seima-Turbino period individuals were diverse in their ancestry, also harbouring DNA from Indo-Iranian-associated pastoralists and from a range of hunter-gatherer groups. Thus, both cultural transmission and migration were key to the Seima-Turbino phenomenon, which was involved in the initial spread of early Uralic-speaking communities.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09189-3
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09189-3
Nature:《自然》,创刊于1869年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:69.504
官方网址:http://www.nature.com/
投稿链接:http://www.nature.com/authors/submit_manuscript.html
