中国地质大学孙祥团队揭示了氧化沉积物再循环是俯冲后斑岩铜形成的驱动因素。这一研究成果于2025年7月4日发表在《科学进展》杂志上。
俯冲后斑岩岩浆氧化态升高和斑岩铜矿化的机制尚不完全清楚。
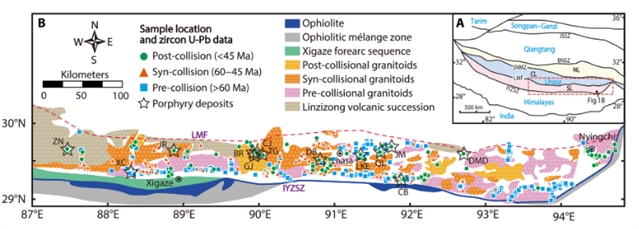
研究组综合分析了藏南冈底斯带东部岩浆岩碰撞前后、碰撞前后和碰撞前后的微量元素和镁汞同位素组成。研究结果表明,从新特提斯俯冲到碰撞后,岩浆氧化态的增加与陆生沉积的富集有关,碰撞后斑岩(Δ199Hg = - 0.25 ~ 0.22‰)和幔源超晚叠岩(Δ199Hg = - 0.54 ~ 0.25‰)中汞同位素分异明显,超晚叠岩(δ26Mg = - 0.51 ~ - 0.04‰)的δ26Mg值为负。
这些结果表明,碰撞后岩浆的氧化作用是由来自印度板块的碳酸盐和/或硫酸盐的俯冲作用驱动的,从而增强了金属的富集。这一发现挑战了海洋俯冲作用主要驱动斑岩铜矿形成的传统观点,突出了大陆俯冲作用在成矿模式中的重要性。
附:英文原文
Title: Oxidized sediment recycling as a driver for postsubduction porphyry copper formation
Author: Zhiming Yang, Xiang Sun, Massimo Chiaradia, Yongjun Lu, Runsheng Yin, Zengqian Hou, Huawei Li, Yiwei Zhou
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-04
Abstract: The mechanisms driving the elevated oxidation state of postsubduction porphyry magmas and porphyry copper mineralization are still not fully understood. We present an integrated study of trace elemental and Mg-Hg isotopic compositions of pre-, syn-, and postcollisional magmatic rocks from the eastern Gangdese belt in southern Tibet. Our findings show increased magmatic oxidation states linked to the enrichment of terrigenous sediments from Neo-Tethys subduction to postcollision, as evidenced by distinctive mass-independent Hg isotope fractionation in postcollisional porphyries (Δ199Hg = 0.25 to 0.22‰) and mantle-derived ultrapotassic rocks (Δ199Hg = 0.54 to 0.25‰) and negative δ26Mg values in ultrapotassic rocks (δ26Mg = 0.51 to 0.04‰). These results suggest that oxidation of postcollisional magmas was driven by the subduction of carbonates and/or sulfates from the Indian plate, enhancing metal enrichment. This finding challenges the traditional view that oceanic subduction primarily drives porphyry copper formation, highlighting the significance of continental subduction processes in metallogenic models.
DOI: adx4474
Source: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adx4474
