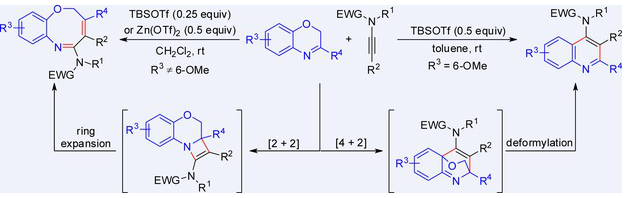
近日,郑州大学王晓娜团队研究了酰胺的可切换环化途径:2h -1,6-苯并恶唑的双催化途径与TBSOTf催化的选择性4-氨基喹啉形成。该成果于2025年7月29日发表在《中国化学》杂志上。
研究组报道了一个依赖底物的环化系统,其中2h -1,4-苯并恶嗪的6个取代基决定了与酰胺的不同途径。非甲氧基底物经TBSOTf/Zn(OTf)-催化[2 + 2]环化/扩环生成2h -1,6-苯并恶唑嗪,而6-甲氧基衍生物通过TBSOTf催化[4 + 2]环化/去甲酰基化途径优先生成4-氨基喹啉。
这种电子效应驱动的选择性在温和的条件下以高保真度工作。该方法提供了从相同前体中正交获取两种重要的药用杂环类的方法,具有广泛的官能团耐受性,具有可扩展性(高达1毫摩尔规模),并消除了过渡金属的需要。选择性可能源于6取代基对中间体的差异稳定。
附:英文原文
Title: Switchable Annulation Pathways of Ynamides: Dual Catalytic Routes to 2H-1,6-Benzoxazocines vs. TBSOTf-Catalyzed Selective 4-Aminoquinoline Formation
Author: Wozheng Fang, Longyu Xiao, Yijie Wang, Junbiao Chang, Xiao-Na Wang
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-29
Abstract: We report a substrate-dependent annulation system where 6-substituents of 2H-1,4-benzoxazines dictate divergent pathways with ynamides. Non-methoxy substrates undergo TBSOTf/Zn(OTf)-catalyzed [2 + 2] annulation/ring expansion to form 2H-1,6-benzoxazocines, while 6-methoxy derivatives preferentially yield 4-aminoquinolines via a TBSOTf-catalyzed [4 + 2] annulation/deformylation pathway. This electronic effect-driven selectivity operates under mild conditions with high fidelity. The method provides orthogonal access to two medicinally important heterocycle classes from identical precursors, features broad functional group tolerance, demonstrates scalability (up to 1mmol scale), and eliminates the need for transition metals. The selectivity may originate from the differential stabilization of intermediates by the 6-substituent.
DOI: 10.1002/cjoc.70199
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cjoc.70199
Chinese Journal of Chemistry:《中国化学》,创刊于1983年。隶属于Wiley,最新IF:5.4
官方网址:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/16147065
投稿链接:https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/cjoc
