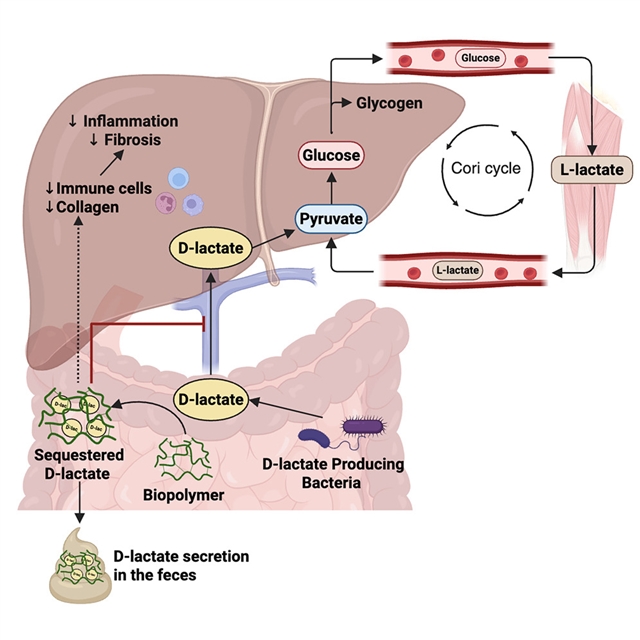
加拿大麦克马斯特大学Jonathan D. Schertzer小组的一项最新研究探明了微生物群中D-乳酸的肠道底物陷阱改善肥胖小鼠的血糖和脂肪肝疾病。相关论文于2025年7月29日发表在《细胞—代谢》杂志上。
课题组发现,人类和肥胖小鼠的循环D-乳酸水平更高。D-乳酸比等摩尔L-乳酸更能提高小鼠肝糖原、甘油三酯和血糖。稳定同位素分析表明,D-乳酸在小鼠和肝细胞中代谢为丙酮酸、TCA中间体、脂质和葡萄糖。肠道菌群是血液D-乳酸的主要来源。用一种产生D-乳酸的菌株定植小鼠,使其血糖比产生L-乳酸的菌株更高。口服一种生物相容性聚合物,可以捕获肠道D-乳酸,迫使粪便排泄,以聚合物长度和剂量依赖的方式降低肥胖小鼠的血糖和胰岛素抵抗。这种D-乳酸陷阱降低了代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝病(MAFLD)/代谢功能障碍相关脂肪性肝炎(MASH)小鼠的肝脏炎症和纤维化。因此,微生物来源的D-乳酸有助于宿主葡萄糖和脂质代谢,可以被捕获以改善肥胖期间的代谢性疾病。
据介绍,L-乳酸参与代谢,包括Cori循环,但对D-乳酸知之甚少。
附:英文原文
Title: Gut substrate trap of D-lactate from microbiota improves blood glucose and fatty liver disease in obese mice
Author: Han Fang, Fernando F. Anhê, Dana Kukje Zada, Nicole G. Barra, Rodrigo Rodrigues e-Lacerda, Breanne T. McAlpin, Ryan Wylie, Line Berthiaume, étienne Audet-Walsh, Conor O’Dwyer, Peyman Ghorbani, Morgan D. Fullerton, Claudia Gagnon, André Tchernof, André Marette, Jonathan D. Schertzer
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-29
Abstract: L-lactate participates in metabolism, including the Cori cycle, but less is known about D-lactate. We found that circulating D-lactate was higher in humans and mice with obesity. D-lactate increased hepatic glycogen, triglycerides, and blood glucose more than equimolar L-lactate in mice. Stable isotope analyses showed that D-lactate is metabolized in mice and in hepatocytes to pyruvate, TCA intermediates, lipids, and glucose. The gut microbiota is the main source of blood D-lactate. Colonization of mice with a bacterial strain that produced D-lactate elevated blood glucose more than an L-lactate producer. Oral delivery of a biocompatible polymer that traps gut D-lactate, forcing fecal excretion, lowered blood glucose and insulin resistance in obese mice in a polymer length- and dose-dependent manner. This D-lactate trap lowered hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in mice with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)/metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). Therefore, microbial-derived D-lactate contributes to host glucose and lipid metabolism and can be trapped to improve metabolic disease during obesity.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2025.07.001
Source: https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/abstract/S1550-4131(25)00328-6
Cell Metabolism:《细胞—代谢》,创刊于2005年。隶属于细胞出版社,最新IF:31.373
官方网址:https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/home
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/cell-metabolism/default.aspx
