近日,美国达特茅斯学院Katherine A. Mirica团队实现了基于导电金属-有机框架的电子纺织品作为水中毒性含氧阴离子的清除剂和传感器。相关论文于2025年7月28日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
有毒氧离子污染对生态系统和人类健康构成严重威胁。虽然各种吸附剂已被开发用于氧阴离子隔离,但设计一种同时实现高选择性,快速吸附动力学和实时传感能力的单一材料仍然是一个挑战。
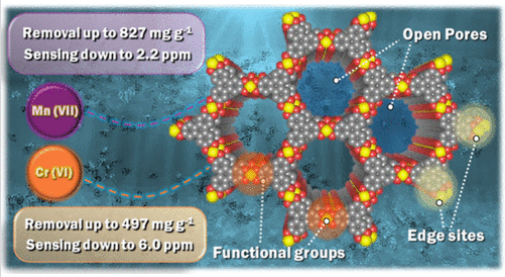
研究组探索了层状导电金属有机框架(cMOFs)的第一个主题,该框架基于六羟基和六胺基三苯基(HHTP和HITP)芯,与镍和铜配合,用于双重传感和过滤水中的氧离子。对Ni3(HHTP)2、Cu3(HHTP)2、Ni3(HITP)2和Cu3(HITP)2的系统研究表明,Ni3(HITP)2表现出前所未有的吸附能力,每克MOF可吸附高达827毫克的MnO4-和497毫克的Cr2O72-,同时在10分钟内过滤掉99%的氧化离子。
Ni3(HITP)2在实际应用中也表现出很高的适用性,在各种水基质、pH条件和竞争阴离子干扰下都保持着卓越的吸附性能。光谱和计算研究揭示了一个多机制的清除过程,包括化学吸附、物理吸附和氧化还原反应。通过将Ni3(HITP)2层层接枝到棉织物上,可以获得机械性,易于操作和柔性的电子纺织品,能够过滤氧化离子长达32次循环而不损失性能,同时允许其检测具有高灵敏度和低检测限,MnO4-为2.2 ppm, Cr2O72-为6 ppm。综上所述,这些发现为基于MOF的下一代水处理技术铺平了道路,该技术集成了高效过滤和实时传感功能。
附:英文原文
Title: Electronic Textiles Based on Conductive Metal–Organic Frameworks as Scavengers and Sensors of Toxic Oxyanions from Water
Author: Patrick Damacet, Priyanshu Chandra, Emma K. Ambrogi, Hyuk-Jun Noh, Ericka L. Asmus, Elissa O. Shehayeb, Giovanni Barcaro, Susanna Monti, Katherine A. Mirica
Issue&Volume: July 28, 2025
Abstract: Water contamination by toxic oxyanions poses a severe threat to ecosystems and human health. While various adsorbents have been developed for oxyanion sequestration, designing a single material that simultaneously achieves high selectivity, rapid adsorption kinetics, and real-time sensing capabilities remains a challenge. This study explores the first use of layered, conductive metal–organic frameworks (cMOFs) based on hexahydroxy- and hexaimino-triphenylene (HHTP and HITP) cores coordinated with nickel and copper for the dual sensing and filtration of oxyanions from water. Systematic investigations of Ni3(HHTP)2, Cu3(HHTP)2, Ni3(HITP)2, and Cu3(HITP)2 reveal that Ni3(HITP)2 exhibits unprecedented adsorption capacities, capturing up to 827 mg of MnO4– and 497 mg of Cr2O72– per gram of MOF, while filtering up to 99% of these oxyanions within 10 min of exposure. Ni3(HITP)2 also demonstrates high applicability in real-world scenarios, maintaining a remarkable adsorption performance across various water matrices, pH conditions, and competing anion interferences. Spectroscopic and computational investigations reveal a multimechanistic scavenging process involving chemisorption, physisorption, and redox reactions. Grafting Ni3(HITP)2 onto cotton textiles via a layer-by-layer approach yields mechanically robust, easy to handle, and flexible electronic textile capable of filtering oxyanions for up to 32 cycles without performance loss, while allowing their detection with high sensitivity and low detection limits reaching 2.2 ppm for MnO4– and 6 ppm for Cr2O72–. Taken together, these findings pave the way for MOF-based next-generation water treatment technologies that integrate efficient filtration and real-time sensing capabilities.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c05275
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/jacs.5c05275
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
