近日,福州大学杨黄浩团队报道了打破内体屏障:硫醇介导的脂质纳米颗粒用于有效的mRNA疫苗递送。这一研究成果于2025年7月22日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
脂质纳米颗粒(LNPs)是临床上最先进的mRNA治疗递送平台;然而,它们的全部潜力受到细胞内mRNA递送不理想的显著限制。
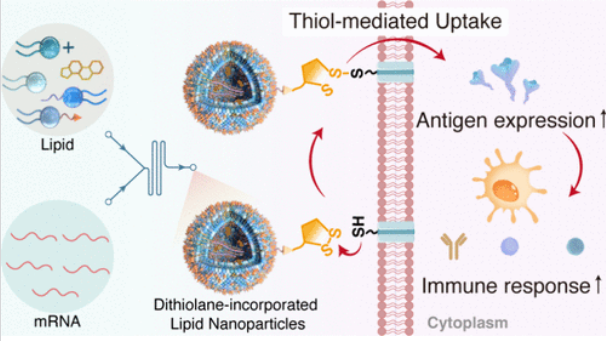
研究组报告了合理的化学设计和合成二硫烷结合的脂质(S-DOPE),以构建一种创新的LNP配方,称为SLNP,用于增强细胞内mRNA的传递。这些化学工程SLNPs利用了固有的硫醇介导的摄取机制,其中独特的二硫烷片段触发了与细胞表面硫醇的动态共价二硫化物-硫醇交换反应。这种化学驱动的反应促进了直接的细胞质内mRNA传递,有效地绕过了内体包裹,这是传统LNPs的主要瓶颈。体外研究表明,与标准LNPs相比,SLNP配方的mRNA转染和翻译效率提高了11倍。
此外,体内评估显示mRNA表达和免疫反应增强4.5倍。低剂量SLNP介导的疫苗接种可引起高滴度的中和抗体和Th1偏倚的T细胞反应。值得注意的是,SLNPs诱导的针对SARS-CoV-2刺突蛋白的中和抗体滴度与使用高剂量的常规LNPs所达到的抗体滴度相当,这突出了其巨大的剂量节约潜力。这些发现表明,SLNP利用化学上创新的硫醇介导摄取机制,为提高mRNA疫苗的有效性和安全性提供了一种有前景的、化学上独特的策略,这在疫苗供应有限的情况下尤其有价值,并可最大限度地减少与高剂量疫苗相关的潜在不良反应。
附:英文原文
Title: Breaking Endosomal Barriers: Thiol-Mediated Uptake Lipid Nanoparticles for Efficient mRNA Vaccine Delivery
Author: Zhijie Lian, Lingying Zheng, Shuya Liu, Junjie Zhang, Jie Zhou, Junjun Wu, Songying Ouyang, Jingying Li, Huanghao Yang
Issue&Volume: July 22, 2025
Abstract: Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are the most clinically advanced delivery platforms for mRNA therapeutics; however, their full potential is significantly limited by suboptimal intracellular mRNA delivery. Herein, we report the rational chemical design and synthesis of a dithiolane-incorporated lipidoid (S-DOPE) to construct an innovative LNP formulation, termed SLNP, for enhanced intracellular mRNA delivery. These chemically engineered SLNPs exploit an inherent thiol-mediated uptake mechanism, whereby the unique dithiolane moiety triggers a dynamic covalent disulfide-thiol exchange reaction with cell surface thiols. This chemically driven reaction facilitates direct cytosolic mRNA delivery, effectively bypassing endosomal entrapment, a major bottleneck for conventional LNPs. In vitro studies demonstrate that SLNP formulations achieve an 11-fold increase in mRNA transfection and translation efficiency compared to standard LNPs. Furthermore, in vivo evaluations reveal a 4.5-fold enhancement in mRNA expression and robust immune responses. SLNP-mediated vaccination at low doses elicits high titers of neutralizing antibodies and a Th1-biased T-cell response. Notably, SLNPs induce neutralizing antibody titers against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein that are comparable to those achieved with significantly higher doses of conventional LNPs, highlighting their substantial dose-sparing potential. These findings establish that SLNP, by leveraging the chemically innovative thiol-mediated uptake mechanism, offers a promising and chemically distinct strategy to enhance both the efficacy and safety of mRNA vaccines, which is particularly valuable in scenarios of limited vaccine supply and for minimizing potential adverse effects associated with high vaccine dosages.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c05367
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c05367
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
