电压成像显示海马抑制动力学形成锥体记忆编码序列,这一成果由加州大学Peyman Golshani研究小组经过不懈努力而取得。2025年7月22日,国际知名学术期刊《自然—神经科学》发表了这一成果。
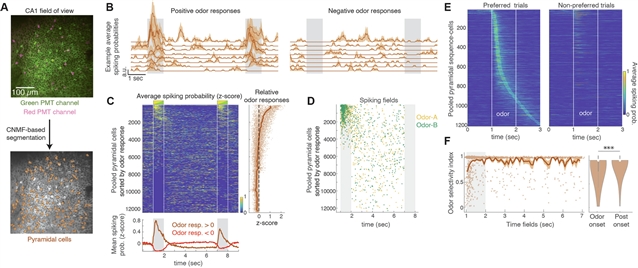
该课题组人员对执行气味提示工作记忆任务的小鼠进行了CA1小白蛋白和生长抑素表达中间神经元的纵向电压成像。与在延迟期间编码气味和时间的锥体气味特异性序列不同,中间神经元编码气味传递,但不编码气味身份或延迟时间。气味触发的抑制作用由数天内数量稳定的中间神经元发挥,细胞不断更新,独立于任务训练。在气味发作时,小白蛋白中间神经元的短暂尖峰随后是广泛的超极化和同步的θ -节律反弹尖峰。
电生理学、光遗传学和钙成像证实,小白蛋白中间神经元在气味传递过程中沉默了大多数锥体细胞,而生长抑素中间神经元抑制了其他中间神经元。少数具有气味选择性的锥体细胞在神经元间超极化后反弹。总的来说,抑制增加了锥体线索表征的信噪比,使记忆相关信息的有效编码成为可能。
据悉,海马体脉冲序列编码并连接行为相关信息。抑制如何塑造这些序列仍不清楚。
附:英文原文
Title: Voltage imaging reveals hippocampal inhibitory dynamics shaping pyramidal memory-encoding sequences
Author: Taxidis, Jiannis, Madruga, Blake, Safaryan, Karen, Dorian, Conor C., Melin, Maxwell D., Day, Zo, Lin, Michael Z., Golshani, Peyman
Issue&Volume: 2025-07-22
Abstract: Hippocampal spiking sequences encode and link behaviorally relevant information across time. How inhibition sculpts these sequences remains unclear. We performed longitudinal voltage imaging of CA1 parvalbumin- and somatostatin-expressing interneurons in mice performing an odor-cued working memory task. Unlike pyramidal odor-specific sequences that encode odor and time throughout a delay period, interneurons encoded odor delivery, but not odor identity or delay time. Odor-triggered inhibition was exerted by stable numbers of interneurons across days, with constant cell turnover, independent of task training. At odor onset, brief spiking of parvalbumin interneurons was followed by widespread hyperpolarization and synchronized theta-paced rebound spiking across interneurons. Electrophysiology, optogenetics and calcium imaging corroborated that parvalbumin interneurons silenced most pyramidal cells during odor delivery, whereas somatostatin interneurons suppressed other interneurons. The few odor-selective pyramidal cells spiked together with interneuronal post-hyperpolarization rebound. Collectively, inhibition increases the signal-to-noise ratio of pyramidal cue representations, enabling efficient encoding of memory-relevant information.
DOI: 10.1038/s41593-025-02016-y
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-025-02016-y
Nature Neuroscience:《自然—神经科学》,创刊于1998年。隶属于施普林格·自然出版集团,最新IF:28.771
官方网址:https://www.nature.com/neuro/
投稿链接:https://mts-nn.nature.com/cgi-bin/main.plex
