近日,中国科学技术大学林岳团队实现了无序Ru-O6八面体通过提高表面氧动力学高效选择性电氧化硫化物生成亚砜。该研究于2025年7月17日发表在《美国化学会志》上。
亚砜是生产各种化学药品和药品的重要中间体,通常通过直接硫化物氧化合成。虽然目前的方法通常需要恶劣的条件和/或有害的氧化剂,但从硫化物到亚砜的电化学转化具有理想的选择性,可持续性和能源效率,同时独特地利用水作为绿色氧源。然而,由于在非水条件下缓慢的表面氧化动力学,实现有效的电有机转化一直具有挑战性。
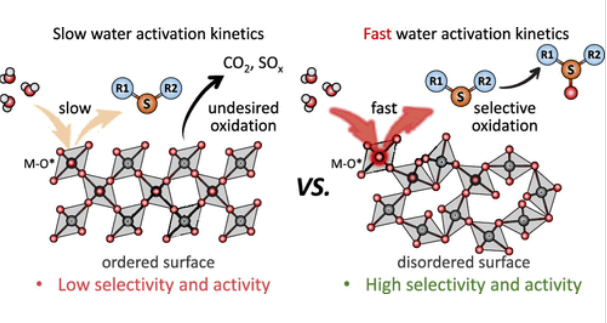
研究组报道了一种新型非晶氧化钌催化剂的发展,其特征是无序连接的规则/不规则的Ru-O6八面体。这种独特的表面结构显著提高了非水介质中地表水的氧化动力学,使通用的电氧化方法能够有效地将硫化物转化为亚砜。在温和的条件下取得了优异的性能(例如,将甲基苯基硫醚转化为甲基苯基亚砜的选择性为99%,收率为98%,法拉第效率为95%),并且该方法适用于广泛的硫化物底物和药物。高电流密度(>100 mA/cm2)下的可扩展产品(12.95 g, 88% FE)进一步证明了这种电催化合成方法的实用价值。
机制和理论研究阐明了无序排列的Ru-O八面体单元在增强费米能级附近的键轨道分布和电子耦合方面的关键作用,从而提高了地表水氧化(*OH→*O)和随后的硫化物氧化(*O + MPS→*MPSO)的动力学,这遵循吸附物演化机制介导的Eley-Rideal反应(AEM-ER)途径。该结果突出了原子无序在克服催化剂优化过程中常见的动力学限制方面的独特而有效的作用,从而实现了理想的非水介质中有机物的直接选择性电氧化。
附:英文原文
Title: Disordered Ru–O6 Octahedrons for Efficient and Selective Electro-oxidation of Sulfide to Sulfoxide via Boosted Surface Oxygen Kinetics
Author: Pan Ran, Mingzi Sun, Aoqian Qiu, Xiao Han, Bailin Tian, Beiyao Xiang, Fangyuan Wang, Xinrui Xu, Luhan Dai, Haowen Zhang, Yang Lv, Yue Lin, Bolong Huang, Mengning Ding
Issue&Volume: July 17, 2025
Abstract: Sulfoxides are essential intermediates for the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals, typically synthesized via direct sulfide oxidation. While current methods generally require harsh conditions and/or hazardous oxidants, electrochemical conversion from sulfide to sulfoxide promises ideal selectivity, sustainability, and energy efficiency while uniquely utilizing water as the green oxygen source. However, achieving efficient electro-organic conversion has been challenging due to sluggish surface oxygenating kinetics under nonaqueous conditions. Here we report the development of a novel amorphous ruthenium oxide catalyst characterized by disorderly connected regular/irregular Ru–O6 octahedra. This unique surface structure significantly boosts the surface water oxidation kinetics in nonaqueous media, enabling a universal electro-oxidation approach for efficient sulfide-to-sulfoxide conversion. Superior performance was achieved under mild conditions (e.g., 99% selectivity, 98% yield, and 95% Faradaic efficiency for methyl phenyl sulfide to methyl phenyl sulfoxide), and this approach applies to a broad scope of sulfide substrates and pharmaceuticals. Scalable productions (12.95 g, 88% FE) under high current densities (>100 mA/cm2) further demonstrate the practical values of this electrocatalytic synthetic methodology. Mechanistic and theoretical investigations elucidate the critical role of disorderly arranged Ru–O octahedral units in enhancing the distributions of bonding orbitals and electronic coupling near the Fermi level, leading to boosted kinetics of surface water oxidation (*OH → *O) and subsequent sulfide oxidation (*O + MPS → *MPSO), which follow an adsorbate evolution mechanism-mediated Eley–Rideal reaction (AEM-ER) pathway. Our results highlight the unique and effective role of atomic disorder in overcoming common kinetic limitations during catalyst optimization, which enables ideal direct selective electro-oxidation of organics in nonaqueous media.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c04028
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c04028
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
