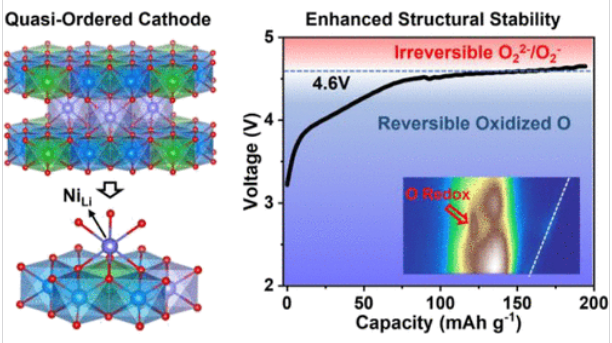
近日,北京大学潘锋团队研究了具有高可逆氧阴离子氧化还原化学性质的准有序富锰阴极。相关论文于2025年7月15日发表于《美国化学会志》。
富锂锰基层氧化物阴极中的阴离子氧氧化还原化学是提高下一代锂离子电池能量密度的一种变革性方法。然而,传统的氧氧化还原反应往往在高压下诱导氧二聚化,导致不可逆的晶格氧损失和快速的电压衰减。
研究组通过一种新的准有序结构设计实现了高度可逆的氧氧化还原化学,该结构包含了层内和层间阳离子无序构型。这种独特的结构显著提高了晶格氧的稳定性,有效地稳定了氧化氧,抑制了过氧或超氧类物质的形成,从而使阴离子氧化还原反应即使在深度氧化状态下也能进行可逆反应。
准有序设计减轻了不可逆相变,并在整个延长循环过程中保持了结构的完整性。因此,所提出的阴极具有优异的可循环性,容量和电压衰减可以忽略不计,在长期循环后保持99%的容量和98%的平均电压。这项工作为解决与晶格氧不稳定性相关的问题以及开发用于先进电池的长寿命、高能量密度阴离子氧化还原正极材料的改造策略提供了新的见解。
附:英文原文
Title: A Quasi-Ordered Mn-Rich Cathode with Highly Reversible Oxygen Anion Redox Chemistry
Author: Weiyuan Huang, Jimin Qiu, Zengqing Zhuo, Jianguo Wen, Yaqing Guo, Yifei Yuan, Zhefeng Chen, Jiangtao Hu, Tianyi Li, Lirong Zheng, Lunhua He, Jinghua Guo, Mingjian Zhang, Feng Pan, Khalil Amine, Tongchao Liu
Issue&Volume: July 15, 2025
Abstract: Anionic oxygen redox chemistry in Li-rich Mn-based layer oxide cathodes represents a transformative approach for boosting the energy density of next-generation lithium-ion batteries. However, conventional oxygen redox reactions often induce oxygen dimerization at high voltages, leading to irreversible lattice oxygen loss and a rapid voltage fade. Herein, we achieve highly reversible oxygen redox chemistry through a new quasi-ordered structural design that incorporates both intra- and interlayer cation disorder configurations. This unique structure significantly enhances lattice oxygen stability, effectively stabilizes oxidized oxygen, and inhibits the formation of peroxo- or superoxol-like species, thereby enabling anionic redox reactions to proceed reversibly even at deep delithiation states. The quasi-ordered design mitigates irreversible phase transitions and preserves the structural integrity throughout extended cycling. Consequently, the proposed cathode demonstrates exceptional cyclability with negligible capacity and voltage fade, retaining 99% capacity and 98% average voltage after long-term cycling. This work provides fresh insights into addressing issues related to lattice oxygen instabilities and reforming strategies for developing long-life, high-energy-density anionic redox cathode materials for advanced batteries.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03271
Source: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jacs.5c03271
JACS:《美国化学会志》,创刊于1879年。隶属于美国化学会,最新IF:16.383
官方网址:https://pubs.acs.org/journal/jacsat
投稿链接:https://acsparagonplus.acs.org/psweb/loginForm?code=1000
