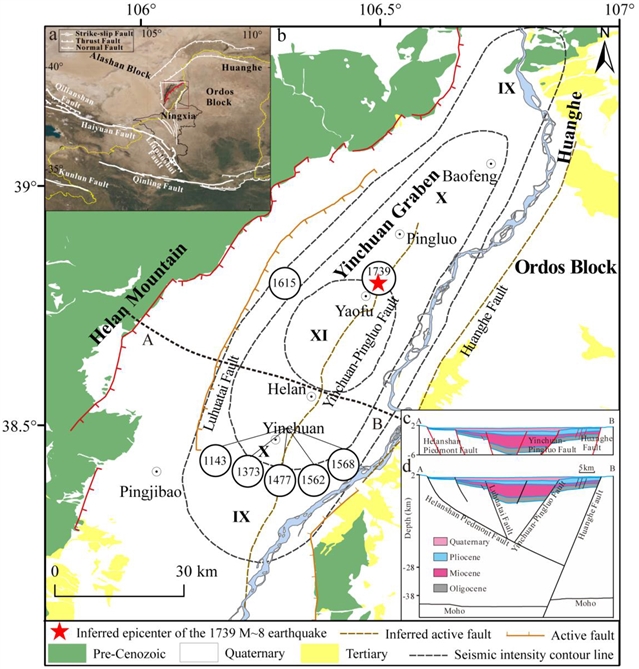
中国科学院青藏高原研究所何建坤团队近日实现了用三维有限元弹性动力学模型重新评价宁夏平罗1739 M~8地震破裂断层。相关论文于2025年7月14日发表在《大地测量与地球动力学》杂志上。
1739年平罗M8级地震发生在银川地堑周围,西与贺兰山交界,东与鄂尔多斯地块交界。地震观测表明,地表断层位移约为2 ~ 3 m,主要沿贺兰山山前断层进行倾滑运动。然而,记录的地震烈度主要分布在盆地内,在贺兰山山前断裂上表现出明显的不对称性。然而,地震断层的一般模式仍在争论中。
研究组建立了三维弹动力有限元模型,对断裂机理进行了重新评价。在该模型中,基于现有观测资料和地震标度规律的综合破裂模型预测,以分裂节点技术为输入,并考虑盆地沉积物对弹性波传播的影响。数值计算结果表明,当贺兰山山前断裂带为大角度(70°)正断层发生地震时,即使考虑了沉积物放大的影响,由模拟的峰值地速度和峰值地加速度预测的地震震动也难以与观测结果拟合。
为了更好地拟合观测到的震动模式,贺兰山山前断裂在8 ~ 27 km深度之间的倾角应小于35°,同震滑动可能达到6 m左右。这一结果使他们得出结论,1739 M~8大地震可能发生在一个表型正断层上,这与最近地震反射探测所证实的贺兰山山前断层的几何形状一致。这一结论意味着,在陆内背景下,沿地下方向减小断层倾角可以增大弹性嵴内断层的宽度,使地表断裂与等震线错位,相对于简单的高角度断裂,地震震级上限增大。
附:英文原文
Title: Reappraising the rupture fault of the 1739 M~8 Pingluo earthquake (Ningxia Province) from 3D finite-element elastodynamic modeling
Author: Jiankun He a b
Issue&Volume: 2025/07/14
Abstract: The 1739 M~8 Pingluo earthquake occurred around the Yinchuan Graben, bounded by the Helan Mountains to the west and the Ordos Block to the east. Seismological observations have shown that surface fault displacement reaches about 2–3 m, mainly by dip-slip motion along the Helanshan Piedmont Fault. However, the documented seismic intensity is distributed predominantly within the basin area, exhibiting a sharp asymmetry across the Helanshan Piedmont Fault. Thus, the general pattern of earthquake faulting is still under debate. We built a three-dimensional elastodynamic finite-element model to reappraise the fault mechanism. In the model, predictions from synthetic rupture models, based on available observations and the earthquake scaling law, were used as an input with the split-node technique, and the effect of basin sediment on elastic wave propagation was considered. The numerical results show that if an earthquake occurred on the Helanshan Piedmont Fault characterized by a high-angle (70°) normal fault, earthquake shaking, as predicted from the modeled peak ground velocity and peak ground acceleration, has difficulty fitting the observed result, even when the effect of sediment amplification is considered. To better fit the observed shaking pattern, the dip angle of the Helanshan Piedmont Fault must be less than about 35° between the depths of about 8–27 km, where the coseismic slip may reach about 6 m. This result leads us to conclude that the 1739 M~8 great earthquake likely occurred on a listric normal fault at depth, in agreement with the geometry of the Helanshan Piedmont Fault, as recently evidenced by seismic reflection explorations. This conclusion means that in an intracontinental setting, a reduction in the fault dip angle along the subsurface could increase the width of the fault in the elastic crust, making misalignment between the surface rupture and the isoseismals and resulting in an increase in the upper bound of earthquake magnitude relative to simple high-angle faulting.
DOI: 10.1016/j.geog.2025.04.011
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1674984725000515
Geodesy and Geodynamics:《大地测量与地球动力学》,创刊于2010年。隶属于爱思唯尔出版集团,最新IF:2.4
官方网址:https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/geodesy-and-geodynamics
投稿链接:https://www2.cloud.editorialmanager.com/geog/default2.aspx
